A hybrid solar system combines both on-grid and off-grid systems that involves solar panels, a hybrid inverter, and a battery bank to provide a flexible and reliable energy solution. In addition, the hybrid inverter acts as a battery bank that stores additional energy for future usage. The dual functionality of this system connected to the grid and storing energy for future use ensures an uninterrupted power supply during grid outages.
Let’s focus deeply on the benefits, drawbacks, components, and costs to determine whether a Hybrid solar system is right for you.
Understanding Hybrid Solar System
The hybrid solar system performs the dual role of on-grid and off-grid systems to ensure continuous solar power production. This system can be used during blackouts where consistent power supply is ensured through grid connection.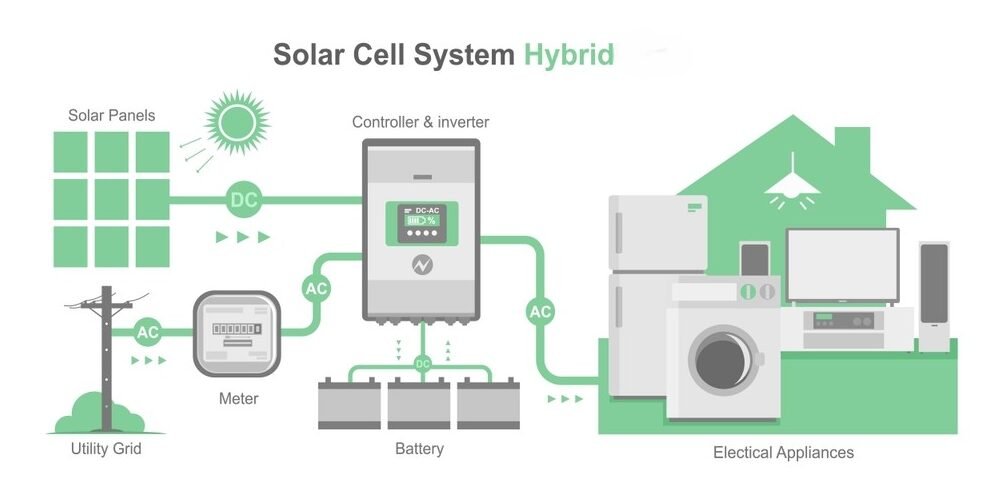
| Features | Grid-Tied System | Off-Grid System | Hybrid System |
| Grid Connection | YES | NO | YES |
| Battery Storage | NO | YES | YES |
| Back-Up Power | NO | YES | YES |
| Net Metering | YES | NO | YES |
| Cost Range | Affordable | Costlier | Moderate |
| Non-Dependent on Energy | Not Fully | Completely | Completely |
| Back up through gas generator | NO | Adaptable | Adaptable |
| Remote Monitoring | YES | Restricted | YES |
| Flexibility | YES | Restricted | YES |
| Suitability | Locations with consistent grid supply and individuals aiming to minimize electricity bill costs. | Rural areas without accessibility to the grid or individuals preferring to opt for Energy-independent methods. | Locations with regular power outages or fluctuating grid supply. |
The functionality of a Hybrid solar system starts with a solar panel that captures sunlight and converts it into DC (Direct Current). Furthermore, the DC power generated by the hybrid solar panels gets converted into AC (Alternating Current) through an inverter, and the extra solar energy generated during the day is stored within a solar battery for usage during nights, cloudy days, or power outages.
A hybrid system benefits homeowners, especially during grid outages or peak demand times through a grid connection. It ensures that when the energy obtained from solar and battery is insufficient, additional power can be drawn from the grid, as well as excess energy is fed to the grid. In other words, a battery functions as an inverter to provide backup power to operate the essential appliances smoothly in your home and working spaces.
Benefits of Hybrid Solar System
The following are the advantages of a Hybrid solar system:
1. Cost Efficiency: Hybrid systems can be cost-efficient on a long-run basis despite their higher upfront costs. This is because the electricity bills will be lowered which helps you save money.
2. Flexibility and Energy Independence: By maximizing the use of solar energy, homeowners will be able to provide sustainable energy by reducing their dependence on the grid.
3. Continuous Power Supply: Compared to traditional systems, Hybrid models supply power continuously due to the batteries connected to the system that accumulate energy. When the sun isn’t shining or during power outages, the stored energy from the battery can be used.
4. Reliable Backup Power During Outages: The battery storage system guarantees a reliable source of power when the grid is down ensuring that your home appliances keep running safely.
5. Advanced Energy Management: The advanced technology in Hybrid systems such as smart inverters that facilitate bidirectional energy flow and battery management systems that optimally utilize energy storage and usage to ensure efficient operation and longer life.
6. Reduced Carbon Footprint: During peak demand or lower output of renewable energy, the stored energy inside the battery is discharged, thereby minimizing the dependence on fossil fuels and reducing the carbon footprint by lowering the emission level.
7. Low Maintenance: Unlike the standard generators, you won’t require paying for fuel and regular maintenance since there are fewer moving parts.
Drawbacks of Hybrid Solar System
The negative characteristics of a Hybrid solar system are:
1. Higher Initial Costs: In comparison to the traditional grid-tied solar energy systems, the upfront costs are higher in hybrid systems due to the added costs of the battery modules, specialized inverters, and a huge number of laborers involved in the installation process.
2. Complexity in Operation: The complicated control process is another major disadvantage of hybrid systems due to the interaction between solar panels, batteries, and the grid requires a cautious approach to production, storage, usage, and availability for future usage.
3. Maintenance and Monitoring Needs: To ensure optimal performance, hybrid solar systems require frequent monitoring and control, which can be an expensive and time-consuming process.
4. Battery Lifespan and Replacement Costs: Batteries don’t have the long lifespan as solar panels and need frequent replacements that might prove to be costly. At times, these changes might affect the efficiency and overall performance of the system leading to long-term costs.
5. Potential Appliance Limitations: A few appliances might not be compatible with the battery and its stored energy, which might restrict the system’s performance.
Components of Hybrid Solar System
These components in a hybrid solar system make the operating process user-friendly:
1. Solar Panels are made up of silicon solar cells that capture the sunlight during the day and convert it into DC electricity through the photovoltaic process.
2. Hybrid Inverters with dual nature convert DC electricity into AC electricity for home usage as well as handling the charging and discharging process of a battery bank. There is a seamless flow of electricity as hybrid inverters are specifically designed to merge both the grid and battery bank, thereby guaranteeing a constant flow of electricity based on your requirements.
3. Battery Bank stores extra energy generated by the solar panels for future use and acts as a reliable power source during nights or power outages. Lithium-ion technology is used in modern battery systems due to its higher energy density and increased longevity compared to traditional battery systems.
4. Mounting Hardware with high quality helps solar panels get strongly installed on the roof or ground at a proper angle and orientation to gain maximum sunlight exposure and be strong enough to resist fluctuating weather conditions.
5. High-quality durable cables are important to handle the current and voltage levels for transferring electricity from solar panels to hybrid inverters and then to the electrical system of your home.
6. Charge Controllers improve the battery lifespan by optimizing the power levels entered inside a battery.
7. Accessories of the hybrid solar system include:
- Monitoring devices analyze and keep track of the performance of solar systems.
- Disconnecting switches and grounding equipment is mandatory for safety and helps the system shut down during maintenance or emergencies.
- Grid Connection is used as an alternative power generation method to draw power from the grid as well as feed additional energy to the grid.
Cost of Hybrid Solar System
The average cost of installing a hybrid solar system ranges between $20,000 to $40,000 based on your system size, location, and specific components used.
The typical cost of a solar system without battery storage is less expensive with a price range of $8,000 to $20,000 without applying any tax credits. In a comparable scenario, the price to install solar panels along with a battery costs between $15,000 and $30,000 after applying the federal tax credits.
For example, several individuals pay around $30,000 for a 6 kW system with monocrystalline panels and three lithium-ion batteries whereas the cost to install a 6 kW system with polycrystalline panels and 1 FLA (Flooded lead) battery is $12,500 approximately. In contrast, the cost of a standard 5 kW solar system costs $10,000 to $20,000 without battery storage.
Potential buyers reduce their upfront costs through federal tax credits and local rebates in the following ways:
Residential Clean Energy Credit: A 30% tax credit is offered for solar panel system installation costs between 2022 and 2032. Gradually, the credit percentage slows down to 26% in 2033 and 22% in 2034.
Local Rebates are one-time incentives for solar installations offered by utilities or government agencies that are deducted from the overall cost of purchasing a solar system or battery storage. Here are a few examples of rebates that vary according to each state in the U.S.:
- Oregon: $2,400 (starting from battery storage systems) to $5,000 (solar panel system).
- Maryland: $1,000 rebate for solar rooftop panels and solar shingle installations exceeding 1 kW.
While estimating the total investment for a hybrid system, consumers should consider certain key factors such as system size, components, installation costs, maintenance and monitoring, local regulations, Return on Investment (ROI), geographical climate, and many more…
Is a Hybrid Solar System right for you?
Yes, If you’re a homeowner, then a Hybrid solar system might be the right choice by considering these primary factors over other types of solar systems:
1. Energy Consumption: Evaluate your household energy usage patterns and peak usage times. Homeowners assess their energy consumption before installing the system in the following ways:
- Calculating utility bills based on the monthly kWh usage and comparing the consumption for at least 12 months. This helps to calculate your per-day energy usage in kilowatt-hours (kWh).
- Preparing a list of electrical appliances in your home helps to provide an estimate of annual energy consumption based on the watt ratings and daily usage (number of hours the devices operated per day).
- Use online solar calculators to determine the recommended size of solar panel system that suits your requirements.
2. Financial Considerations: While considering the financial aspects, you need to keep in mind these factors:
- Expensive initial investment due to the inclusion of batteries:
- Tax credits and rebates to help bring down the upfront costs.
- Return on investment (ROI) to calculate savings on your electricity bills.
- Maintenance costs include the replacement of batteries.
3. Grid Reliability: It is important to consider the reliability of your local power grid and the possibility of net metering.
4. Location: Evaluate the sunlight your location receives and assess the possibility of shading issues.
In conclusion, let’s have a glimpse of the advantages and disadvantages of Hybrid solar systems in different scenarios:
ADVANTAGES:
- Areas with unreliable grid access
- Remote Locations
- Locations with high electricity rates
- Environment conscious zones
DISADVANTAGES:
- Huge space requirements
- Limited battery lifespan
- Complex maintenance process
- Higher upfront costs
Ray is an avid reader and writer with over 25 years of experience serving various domestic and multinational private and public energy companies in the USA.