You can make money from solar power by selling excess electricity back to the grid through net metering, earning solar renewable energy certificates (SRECs), leasing your rooftop to solar companies, and investing in or developing solar farms. These strategies help you generate income while promoting renewable energy use.
As technology has improved and costs have decreased, solar energy has become a more appealing choice for households and businesses.
There are also other methods to generate income from solar power, which we will explore later in this article.

Solar energy typically generates electricity by turning solar light energy into electricity. Flat solar panels can be attached to a building’s roof or arranged across open areas to produce photovoltaic (PV) energy. Another technique, called thermal solar, transforms water into steam using a series of mirrors to concentrate the sun’s energy on a single spot, which drives a turbine. Photovoltaic solar panels are far more widespread than other varieties in residential and commercial settings.
In this article, I have explained how solar energy can provide significant financial benefits. However, these benefits come from saving money rather than making extra money. Keep reading for more details on this topic.
Different Ways to Make Money from Solar Power:-
Tax Incentives
Most state governments provide some tax credit or incentive to promote the more widespread use of solar panels. The total cost after installation can therefore be less than the sticker price. Tax credits offered for solar energy also help lower yearly tax obligations. The easiest way to make money from solar panels on your roof is through net metering.
Net Metering
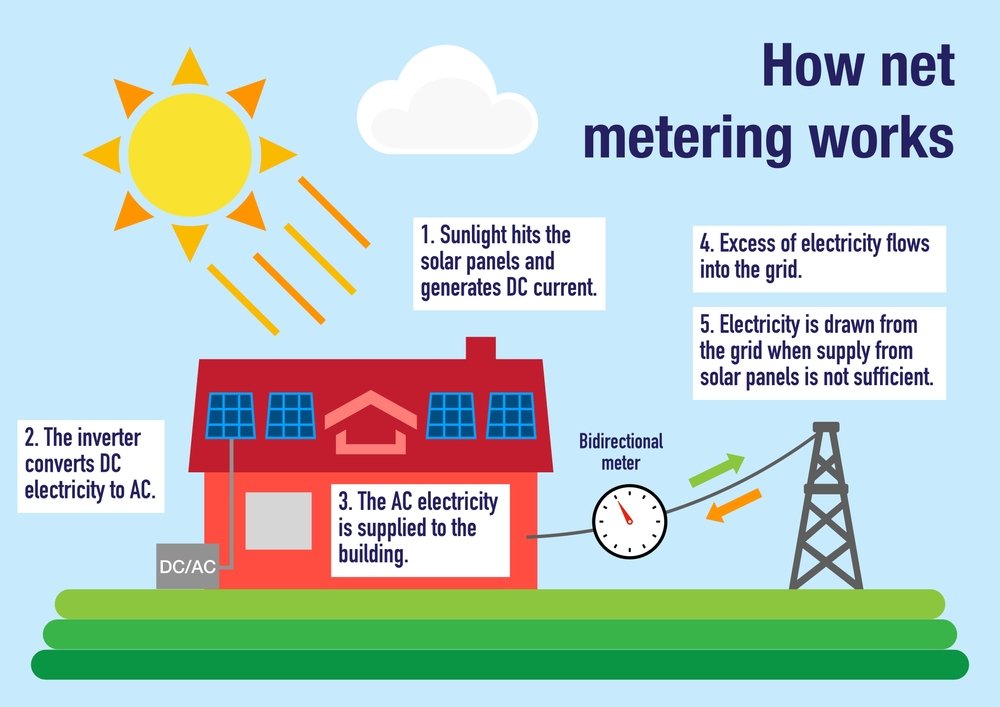
Utility users that produce solar power can feed part of the excess energy back into the grid thanks to net metering. With this billing strategy, solar clients receive credits against their electricity usage, which lowers their monthly expenses. Although net metering laws have been passed in most states, there are still certain states where the benefits still need to be fully realized.
Solar Stock Investments
The Invesco Solar ETF (TAN) is one of the easiest methods to invest in the solar energy industry. Tracking the MAC Global Solar Energy Index is the objective of the ETF. It includes businesses that make solar power systems and products for consumers, businesses that make the tools solar panel manufacturers use, businesses that install solar energy systems, and businesses whose strategy is to focus solely on producing solar cells.
According to the Solar Energy Industries Association, the Solar Investment Tax Credit (ITC), introduced in 2006, has led to an average annual growth rate in solar energy of 52%.
Additionally, the profitability of solar companies is projected to rise as rising demand offsets the supply glut caused by Chinese production.
The Ultimate Money-saving Solution: Net Metering
Being fully off the grid, or having grid independence, may be possible if you live in a remote place. However, staying connected to the current utility grid may make sense for many residential homes with solar energy systems. You can create your energy while being linked to the utility grid and selling excess solar electricity to your neighborhood utility provider.
Although classic net metering is the most common method, various options are available based on where you live, your state, and your utility provider’s policies. These options are helpful if you wish to sell solar energy back to the grid. Which choice is best for you depends on your specific solar configuration and the local utility company.
Using Net meters or Net charging:
In the past, net billing was mostly used in large commercial solar installations, but as more distributed solar energy systems are installed, it is increasingly frequent for residential installations. Like net metering, net billing enables you to use the grid effectively as a storage system for the extra electricity your solar system produces.
A kilowatt-hour produced by your solar panels is worth the same amount as a kilowatt-hour produced by the grid under net metering, where credits are often exchanged on a one-to-one basis. Net billing often results in a lower compensation rate than you would otherwise pay for electricity.
You will often sell the extra energy produced by your solar panels back to your utility at the wholesale rate rather than the retail rate instead of banking the credits gained from those credits.
Purchase or sell all:
In contrast to conventional metering arrangements, the buy all/sell all model enables consumers to sell the utility company 100% of the energy produced by their solar panels. In exchange, they receive their utility’s full retail price for all the energy used in their home. For this kind of net metering, two independent meters are needed, and the user is responsible for paying the difference between the energy generated and used. You don’t directly consume any of the electricity produced by your solar panels when you use to buy all/sell all net metering.
Certificates for Solar Renewable Energy (SRECs):

To reduce the emissions from fossil fuels, many states and other jurisdictions have implemented legislation requiring utility companies to source a certain proportion of their power from renewable energy sources like solar energy. Utility firms may use their renewable energy facilities or purchase renewable energy credits to demonstrate compliance with the mandate.
For every 1,000 kWh (or 1-megawatt hour) of electricity produced by a solar energy system, you may be eligible to get one Solar Renewable Electricity Certificate (SREC) if you reside in an eligible location. SRECs are performance-based solar incentives that “count” towards a state’s percentage of renewable energy. Homeowners can receive credit for adding renewable energy to their state’s grid and reducing their reliance on nonrenewable sources. The electricity produced by your solar system is not included in these SRECs. Either the utility company directly or a particular SREC broker may purchase them.
With Net Metering, How Do Electricity Bills Operate?
My imagination allows me to speak generally for most households that it’s common to have extra electricity production in the summer and more grid usage in the winter. Your utility would only give a monthly check when a house produces what is needed because these production variances are somewhat predictable. Instead, you will accumulate extra credits throughout the summer to use as needed at night and in other seasons like the winter. Even if your solar system produces significantly more energy than you use in certain months and lesser in others, with the appropriate arrangement, your system can generate enough power to match and fulfill your annual electricity consumption.
This is possible as you will be given credit depending on the average number of extra kilowatt-hours generated by your solar unit and you contributed back to the grid for the particular month or time. However, in an equally possible circumstance wherein your solar unit generates less electricity than your required consumption, you will need to purchase electricity from the service provider to compensate for the deficit. In such cases, you would only be responsible for paying for the electricity you consume according to the deficit.
It’s important to note that if you already have a solar photovoltaic array system at your home or are thinking about getting one, you should be aware of how and why you might want to keep your connection to the current electrical grid. Consult your local electric utility as you plan your solar energy system. They already have a plan in place to assist households in producing and reselling renewable energy.
Conclusion
Making money from solar power is not only possible but increasingly accessible thanks to advancements in technology and supportive policies. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, homeowners can save up to $30,000 over 20 years by installing solar panels and participating in net metering programs.
Additionally, the market for solar renewable energy certificates (SRECs) offers an average annual income of $300 to $1,000 per kW of solar capacity. Leasing your rooftop can provide steady rental income, and investing in solar farms can yield significant returns, with solar investments showing average annual growth rates of 11%. As the demand for clean energy continues to rise, these opportunities for generating income from solar power will likely expand further.
Solar firm stocks or ETFs are also a fantastic option for people looking for an investing strategy in the solar industry. Everybody knows future energy will be solar. In 2016, SolarCity was acquired by Tesla Corp., owned by Elon Musk, for $2.6 billion. It’s no longer a secret. Thus one should use it immediately.
Ray is an avid reader and writer with over 25 years of experience serving various domestic and multinational private and public energy companies in the USA.

