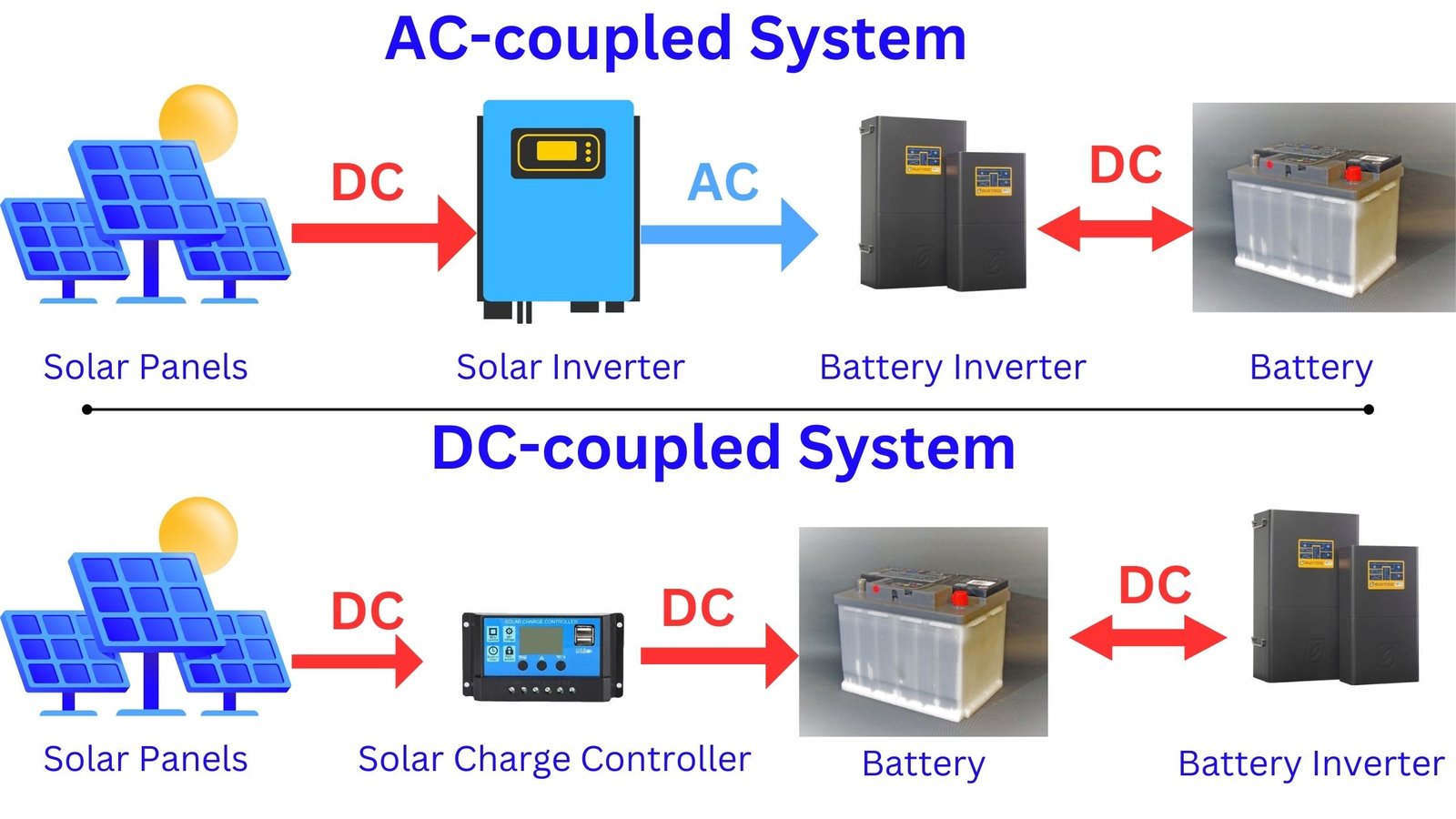
While you are integrating solar batteries with photovoltaic (PV) systems, it is very important to understand the fundamental difference between AC coupling (connecting panels to the battery through an inverter) and DC coupling (connecting panels directly to the battery). Because, these two methods influence how solar energy is stored and consumed, impacting efficiency, installation difficulty, and overall system performance.
AC coupling is the process of connecting solar panels to an inverter which further converts the panel-produced DC (Direct Current) into AC (Alternating Current) before it can reach the energy storage system (Battery). One of the advantages of this setup is solar panels and grid can charge the batteries which allows great flexibility when your solar panels are not generating an expected amount of electricity.
DC Coupling connects your solar panels directly to the battery storage system before it reaches the inverter. Therefore, this configuration naturally enables higher efficiency during the battery charge. Also, during the conversion process, the energy losses during battery charge are greatly reduced.
Understanding this distinction between the AC and DC coupling is important for solar system owners for several reasons such as installation flexibility, system resilience, efficiency consideration, and grid interaction.
The Journey of Electricity in AC and DC Systems
Understanding the journey of electricity from solar panels to storage includes paying attention to AC (Alternating Current) and DC (Direct Current) power systems.
Making it usable for the home, Here are the electricity pathways operating through the system by converting DC to AC:
DC-Coupled System:
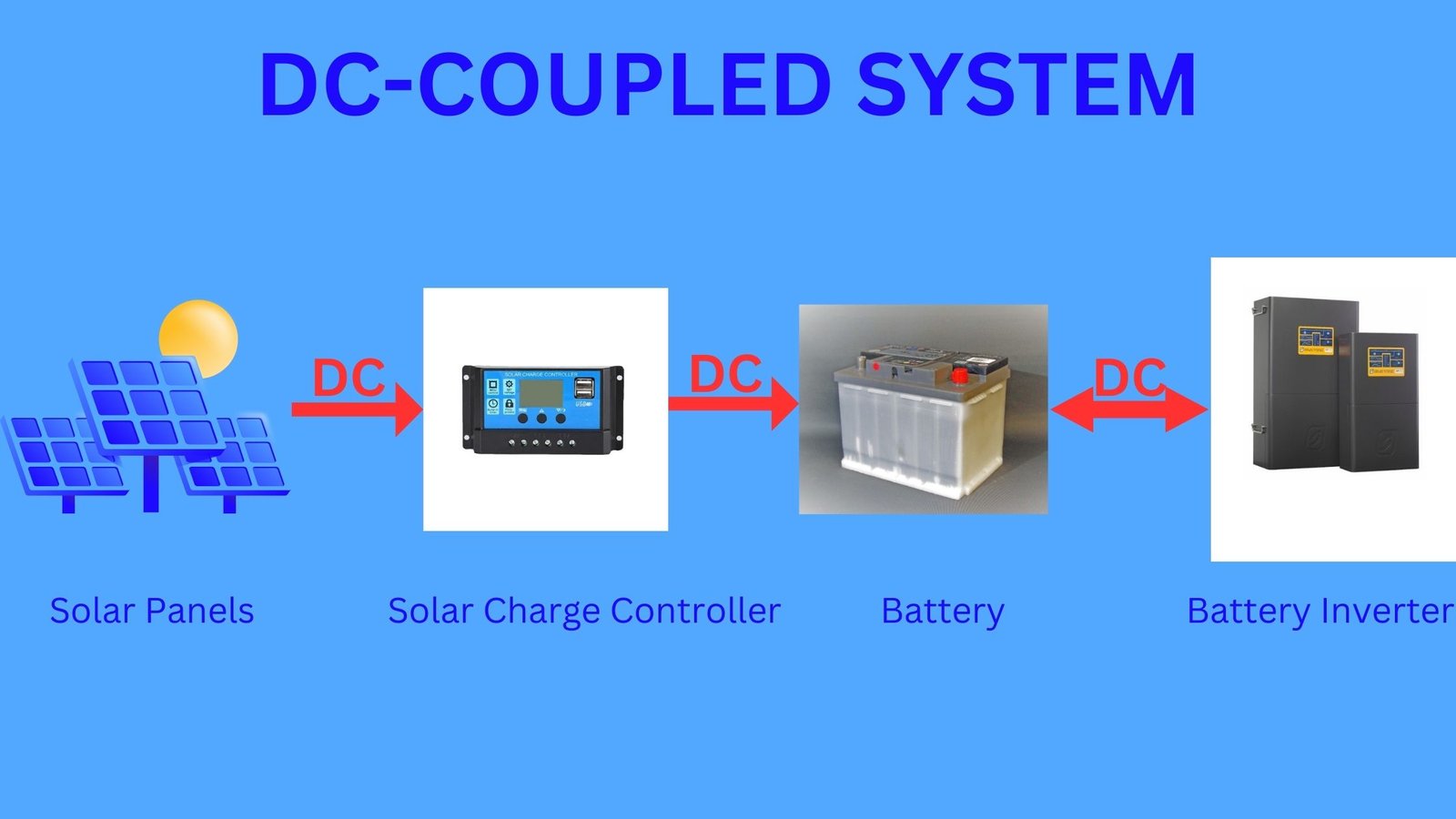
- Generation Process: Solar panels generate DC electricity when a beam of sunlight hits the photovoltaic cells.
- Storage Process: The DC electricity is then transferred to a battery storage system, which stores the energy for later use. Lithium-ion or Lead-acid are batteries that store DC power safely.
AC-Coupled System:
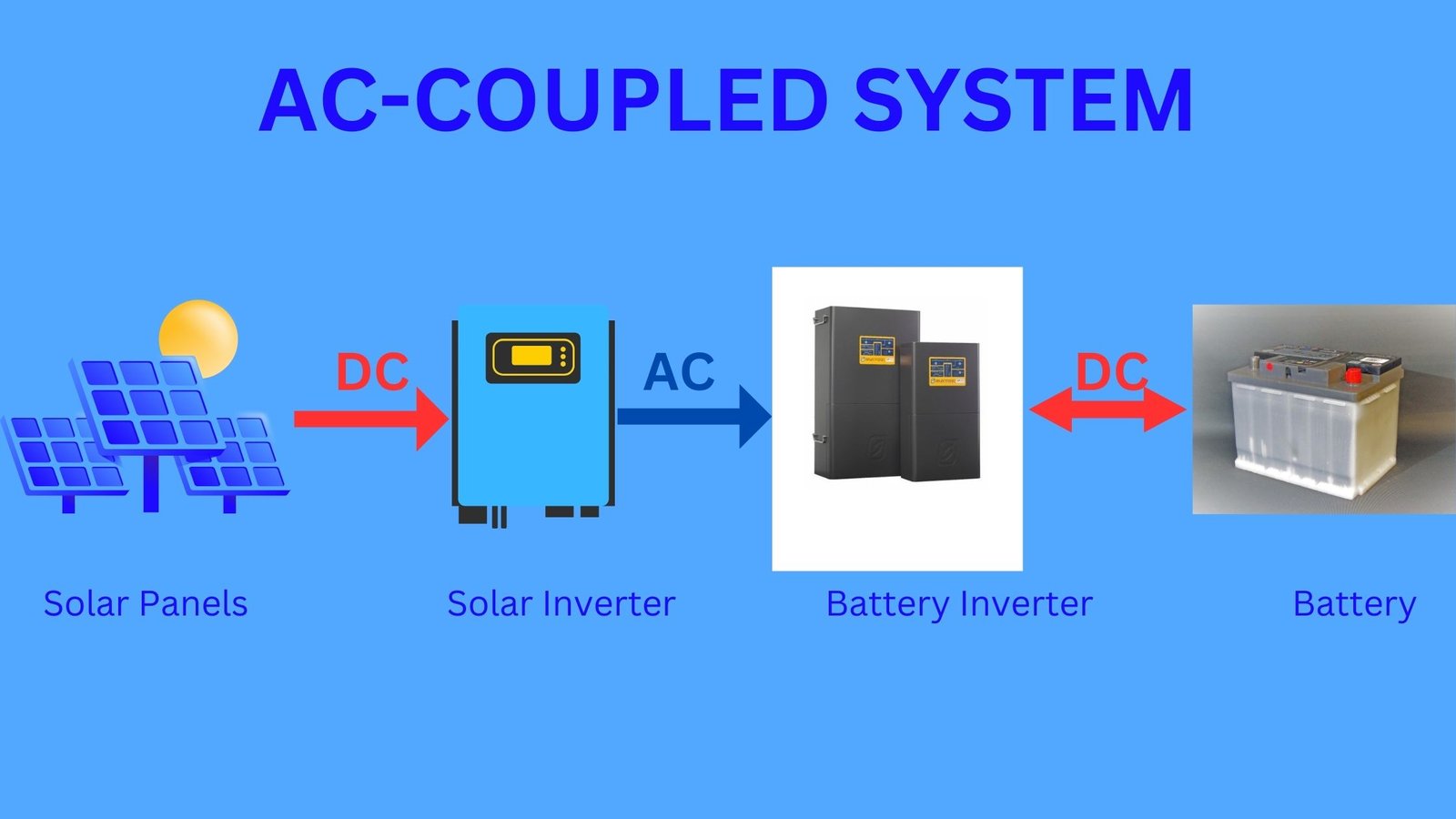
- Conversion Process: For an AC system, firstly the solar panel-generated DC electricity must be converted to AC using an inverter. Following this step is necessary because most of our household appliances as well as the electrical grid operate on AC.
- Storage Process: After the conversion process, the AC electricity can be directly used for the home or else fed to the grid. If you require storage options, then some systems use batteries for storing AC electricity, but this always depends on some extra conversion processes.
DC electricity from solar panels must be converted to AC for home use to ensure compatibility with household appliances and the high effectiveness of energy transfers.
DC-to-AC conversion process impacts system efficiency because inverters have an efficiency rating from 90% to 98%. This simply refers to a small percentage of energy loss during the conversion process which impacts the overall energy yield and system efficiency.
Also, the conversion process of DC to AC impacts system design as it requires additional components for conversion and storage. You must select the perfect inverters, batteries, and wiring systems to handle AC electricity requirements. As a result, combining these components will lead to higher initial costs and maintenance expenses.
Pros and Cons of AC-Coupled Systems
Here are some of the Pros and Cons of AC-coupled systems:
Pros of AC-coupled system:
- System Design adaptability
AC-coupled systems are greatly flexible while working with different energy sources like solar panels and backup generators, which allows easy adaptability to various energy consumption requirements.
- Ability to scale
Easily able to scale up/down allowing to add or remove components without major changes and this is beneficial while energy requirements are increasing.
- Cost-Effectiveness
AC coupling reduces installation costs because existing systems can usually be taken advantage of by eliminating new component requirements and costly modifications.
- Simplifying Maintenance
With AC-coupled systems, the maintenance process is simple because they use common components that can be easily replaced or repaired.
- Improvements to Grid functionality and interaction
AC-coupled systems are capable of working more effectively with the grid as they allow good energy management and enable selling excess electricity back to the utility grid.
Cons of AC-coupled system:
- Loss of Efficiency
AC-coupled systems might struggle with efficiency losses mainly due to the simultaneous and multiple conversions from DC to AC energy which impacts overall system performance.
- Increased Level of Complexity
Integrating multiple energy sources leads to a higher system complexity which is too challenging to implement troubleshooting and repairs.
- Dependability on Inverters
These systems are heavily dependent on inverters for energy conversion, which can become a failure especially when the inverter malfunctions, the performance of the entire system might get compromised.
- Possibilities for Decreasing Performance
Due to fluctuating energy sources and improper management, AC coupling leads to poor performance and results in insufficient energy output.
- More Expensive Initial Costs
Although they are cost-effective in the longer term, AC-coupled systems have higher initial costs compared to other simpler systems, which are likely to demotivate people from adopting them.
Pros and Cons of DC-Coupled Systems
Here are some of the Pros and Cons of DC-coupled systems:
Pros of DC-coupled system:
- Decreases cost of Equipment
DC-coupled systems use a single inverter for solar panels and battery storage, thus reducing equipment costs by eliminating the additional inverters and any other interconnection lines.
- Higher level of Efficiency
There is a very small amount of energy loss because the DC-coupled systems avoid the multiple conversions between AC and DC, and it leads to better overall efficiency in energy storage and usage.
- Excellent Performance in Off-Grid Utilization Conditions
DC-coupled systems are beneficial for off-grid installations, managing energy efficiently from solar panels directly to batteries without having to interact with the grid.
Cons of DC-coupled system:
- Lack of adaptability
DC-coupled systems do not provide the adaptable nature or flexibility of AC-coupled systems especially when multiple energy sources have to be integrated. As a result, it limits options for further expansions or upgrades in the future.
- Level of Complexity in Retrofitting
It can be very complicated to retrofit an existing AC system to a DC-coupled system, and it can be costly too. And, this is because it requires changes to the existing infrastructure.
- Dependency on Charge Controllers
DC-coupled systems are heavily dependent on charge controllers for managing the battery’s charging and discharging. Therefore, it can also cause a failure if the controller malfunctions.
- Possibility of Compatibility Issues
It is not that all solar panels and batteries will be 100% compatible with DC-coupled systems. As a result, it limits certain choices for consumers and requires specific expensive equipment or not available frequently.
- High cost of Initial Setup for Some Configurations
Undoubtedly, they are cost-effective in the long run, but the initial purchasing cost for a DC-coupled system is higher for certain configurations, especially if extra components are needed.
Choosing the Right System for Your Needs
Choosing between AC coupling and DC coupling impacts the efficiency, cost, and overall performance of solar energy systems and battery storage. Here are the factors that influence how owners can determine which system best meets their energy storage and usage requirements.
Factors in Deciding Between AC Coupling and DC Coupling
- System Configuration:
AC Coupling connects the inverter to the AC side of the electrical system where the inverter converts solar panel-generated DC electricity to AC before being used for home usage or feeding back to the grid. Therefore, this setup allows an easy integration with existing AC systems, and it is very flexible for retrofitting into older homes.
DC coupling connects solar panels directly to a battery storage system and allows storing the DC electricity without converting it to AC. And, this leads to higher efficiency due to fewer conversion steps, but it requires more complex system design and compatibility issues.
- Efficiency:
AC Coupling causes additional loss because of multiple conversions from DC and AC, but modern inverters are designed to reduce these losses such that overall efficiency is still high.
DC Coupling offers better efficiency as it reduces conversions, and it is beneficial in systems where battery storage is heavily used because it allows direct charging and discharging of batteries.
- Cost:
AC Coupling has a lower initial cost if integrated with existing AC systems, but the long-term operational costs could be high due to efficiency losses.
DC Coupling has a high upfront cost because it requires specialized equipment for installation but has low operational costs in the future because of its improved efficiency.
To determine whether an AC-coupled system or a DC-coupled system is best suited for their needs, owners should consider the following steps:
- Evaluation of Energy Needs
- Evaluate Existing Infrastructure
- Consider Future Expansion
- Consult with Professionals
- Analyze Cost-Benefit
Ray is an avid reader and writer with over 25 years of experience serving various domestic and multinational private and public energy companies in the USA.