The history of solar energy and solar panels is a fascinating tale of innovation and determination going back to ancient times. Humans first used solar power as early as the 7th century B.C., when they used magnifying glasses to focus sunlight and light fires. This early use of solar energy set the stage for centuries of exploration and development.
Solar energy is a renewable power source acquired from the radiating sunlight. Solar panels, comprised of Photovoltaic cells, capture and utilize this sunlight energy to convert it into electricity, which is known as the Photovoltaic Effect. In simple terms, sunlight generates an electric current when it strikes the PV Cells.
The popularity of solar panels and solar energy usage has immensely increased. According to last year’s report, 3.4% of solar energy contributed to the total electricity generated in the United States.
However, there is no simple answer to questions like “Who invented solar panels” and “When were they invented” because Solar technology has evolved gradually and advancements have been happening throughout the 20th century. In 1954, Bell Labs researchers’ invention of the silicon solar cell was observed as a major milestone that helped make way for more efficiency in practical panels.

Before you explore the evolution of Solar Power and the future of solar energy, it is important to understand the history of solar energy through key historical events crucial from the early years of the 1800s. You must know what solar energy and solar panels are. Also, through key events in history.
Ever since the evolution of Solar Energy and Solar panels, we have witnessed the upgradation over the years – from the early solar cells to the modern, sleek panels. Do you know how much solar energy and solar panels have evolved in the present?
Solar energy ranks among the earliest forms of power generation in the world among the earliest forms of power generation globally. From ancient civilizations using magnifying glasses to concentrate sunlight for fires to the early experiments with photovoltaic cells, the journey of solar energy is rich and diverse.
Detailed History of Solar Energy and Solar Panels:-
Early Years – Before the 1800s
During the era of early years – before the 1800s- People used Sunlight to fire as a source of Light and Heat. The major point throughout ancient history was humans extensively utilized sunlight for many practical purposes like lighting fires and experiencing the benefits of its natural brightness and warmth. Whereas, the Romans, Greeks, and Chinese used Passive Heating Techniques.
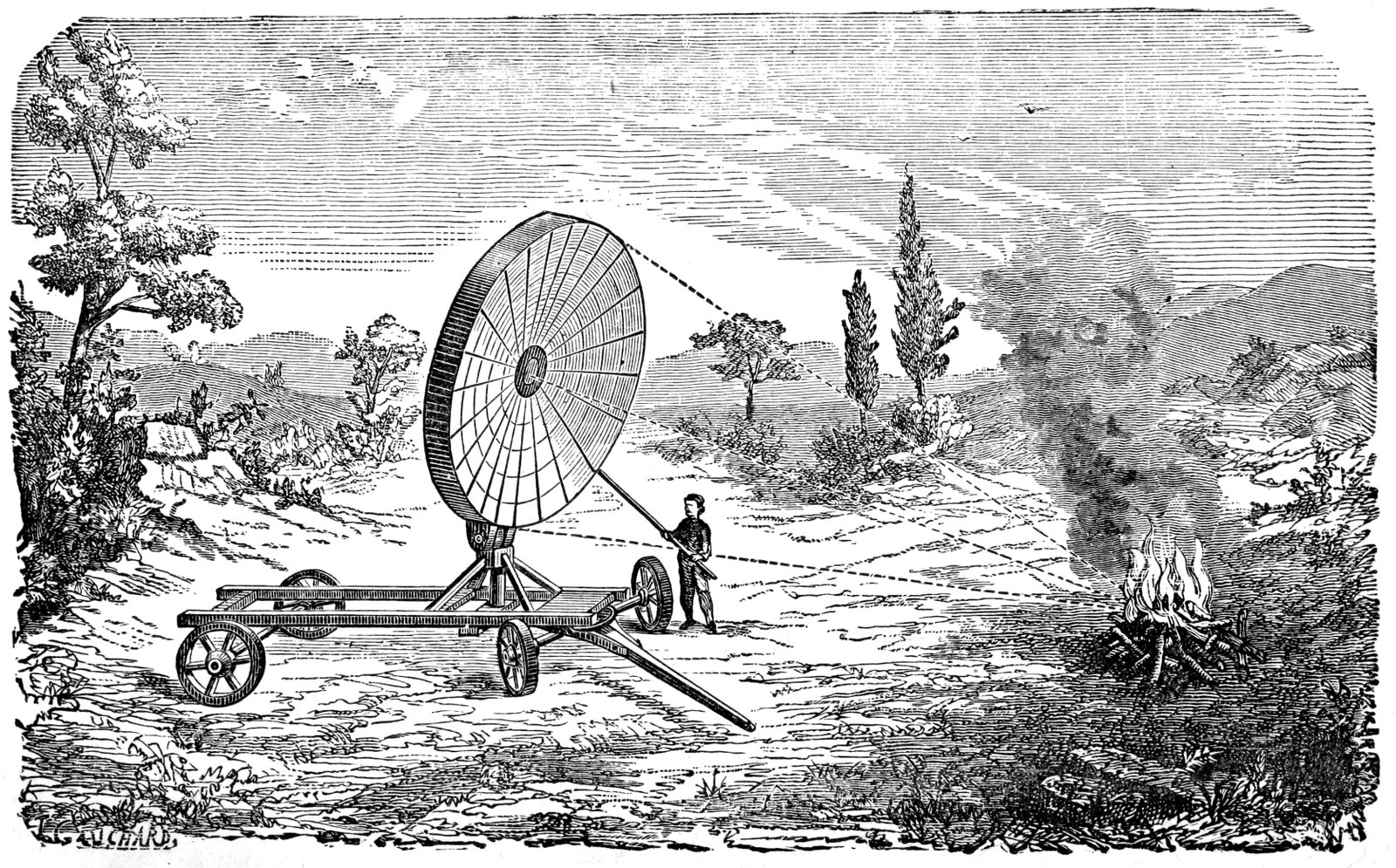
Romans used Burning Mirrors and SunRooms with reflective surfaces to maximize sunlight power to light fire.
- Burning Mirrors are Large reflective surfaces that allow focusing sunlight to create an extreme heating effect. Further, it can be used for various purposes like firing and igniting wooden ships during battles.
- Sunrooms are created spaces with large windows to capture sunlight. Also, it creates indoor warmness – a predecessor to modern-day passive solar architecture.
Greeks used Passive Heating Principles by utilizing architectural design to maximize the exposure of solar and make buildings warmer.
Chinese adopted Passive Solar Design in their homes, to obtain the Sun’s natural warmthness for comfort.
Anasazi Building Cities Beneath South-Facing Cliffs is a clever design that keeps them warm in winter. It shows their smartness and connection to nature.
Ancient Egyptians Evaporated water and Cooled their home by placing water-filled vessels around their homes. As the water evaporated, it removed heat and created coolness.
In 1767, Swiss scientist Horace Benedict de Saussure invented the first solar collector, essentially a solar oven. This pioneering invention laid the groundwork for future advances in solar technology, paving the way for today’s diverse applications, like solar panels and water heaters.
This is the elementary beginnings of solar technology where solar principles implementation was spontaneous and creative.
1800-1900s
The early 19th century – 1800-1990s, saw the first traces of solar energy quest. The efforts constructed a path and considered solar energy a scientific curiosity rather than a practical power source. Here is a concise timeline from where the solar advancement kickstarted.
- 1839: French physicist Edmond Becquerel – The Father of solar energy, discovered the Photovoltaic Effect which was the foundation for converting light into electricity.
- 1873: Willoughby Smith struggled with the concept of the Photoconductivity of Selenium, which paved the way for further exploration.
- 1876: William Grylls Adams and Richard Evans Day demonstrated that selenium can directly generate electricity from light. It is a key advancement to Willoughby Smith’s work.
- 1883: Charles Fritts created the first crude solar cell prototype using selenium, drawing the invention of the first solar panel, though inefficient.
The above 4 milestones symbolize an essential advancement in learning and utilizing the sun’s power. Also, making groundwork for future innovations in solar technology.
1900-2000s
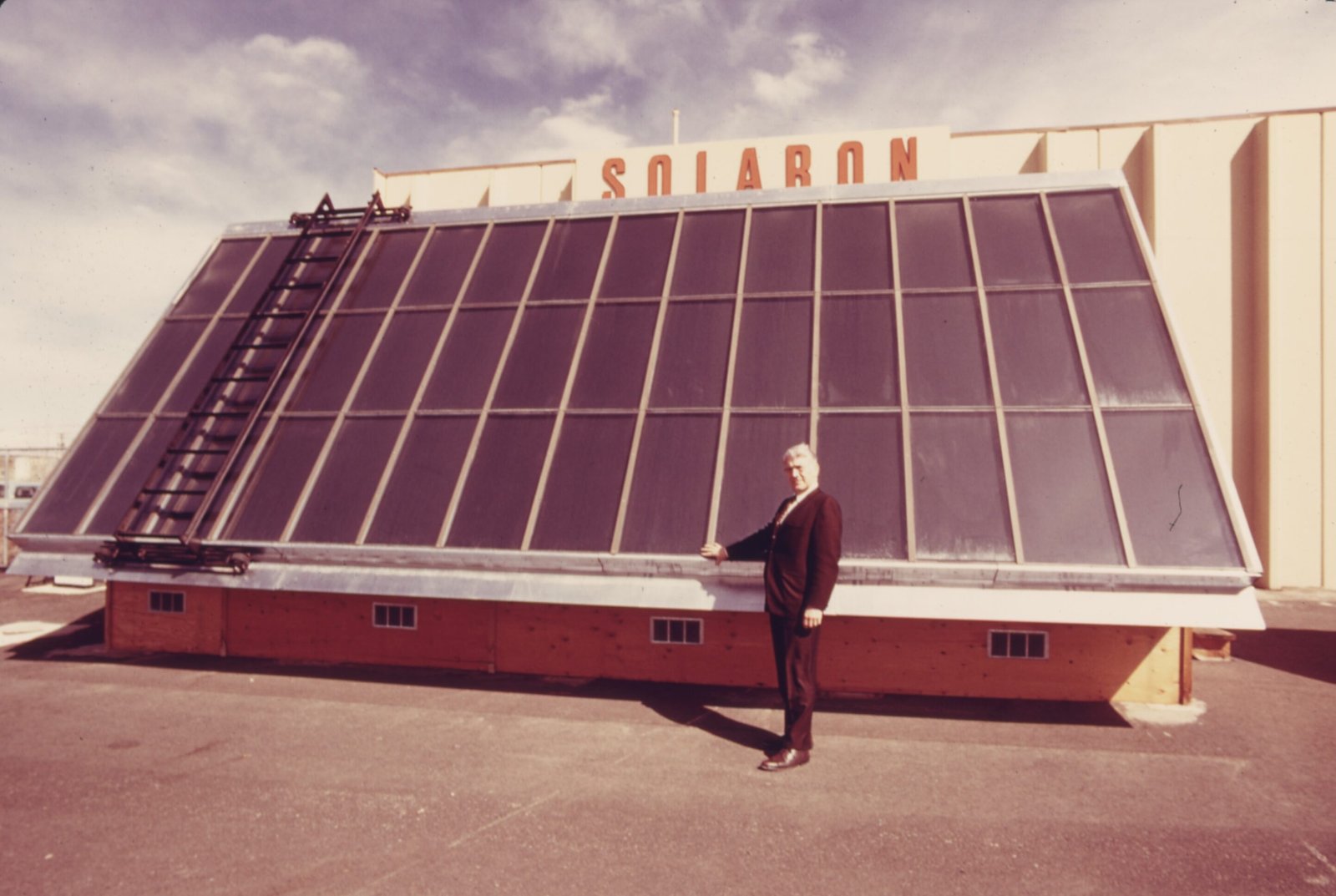
The 20th century – 1900-2000s witnessed the first commercially possible silicon solar cell, with a revolutionary 4% efficiency.
- 1905: Albert Einstein’s Photoelectric Effect laid the basis for understanding solar cells about how they convert light into electricity and function.
- 1939: MIT Solar House 1 was the earliest attempt to blend solar technology into residential architecture. It showcased the solar energy potential for practical applications on a small scale.
- 1954: The first practical Photovoltaic (PV) cell was developed using silicon by the Bell Labs researchers Daryl Chapin, Calvin Fuller, and Gerald Pearson marking a noteworthy milestone in solar technology development.
- 1958: The Vanguard I satellite was the first to use solar panels for power generation in space. Also, succeeding missions like Vanguard II, Explorer III, and Sputnik-3 continued to utilize solar panels.
- 1963: Sharp Corporation achieved a milestone by becoming the first company to mass-produce solar cells and began commercializing solar technology.
- 1964: The Nimbus satellite was launched that included solar panels to generate electrical power for its instruments. Further improved in space exploration and satellite technology.
- 1970: The Energy Crisis and the Environmental Movement are the factors that stimulated interest in renewable energy sources like solar power as an alternative to traditional fossil fuels.
- 1973: The First Solar-Powered Building – Solar One in France, demonstrated the ease of using solar energy for everyday applications.
- 1976: Production of Thin Film Solar Cells offered a flexible and lightweight alternative to traditional solar panels and this innovation expanded the range of solar technology applications.
- 1977: NREL Creation was a leading research institution that focused on advancing renewable energy technologies – including solar power.
- 1978: The Energy Tax Act provided tax credits for solar panel installation to encourage its adoption in the United States.
- 1979: Solar Panels Installed in the White House were a symbol of commitment to renewable energy but were unfortunately taken down in 1981 during successive renovations.
- 1981: Solar Challenger – Solar Powered Aircraft, completed its first flying across the English Channel and emphasized on potential of solar energy for transportation.
- 1982: Quiet Achiever is an Australian solar-powered boat that showed the ease of solar energy for marine transport.
- 1994: Japan’s 70,000 Solar Roofs Program was launched to promote solar panels installation on residential rooftops that would contribute to solar energy growth in the country.
- 1999: Germany’s 100,000 Solar Roofs Program was implemented to encourage solar panel installation in residential as well as commercial buildings and played a vital role in Germany’s emergence.
Therefore, these innovations helped power satellites and remote applications. Also, scientific advancements and manufacturing techniques led to efficiency and cost reductions.
2000- Present
2005: The Investment Tax Credit (ITC) was introduced by the United States to provide financial incentives, and tax credits to businesses and homeowners who invested in solar technologies installations and improved the growth of the solar industry.
2006: California Solar Initiative (CSI) strived to promote the state’s solar installations by offering rebates and incentives. It significantly contributed to California’s leadership in solar capacity and paved the way for similar programs nationwide.
2008: Obama Installed Solar Panels in the White House as adherence to renewable energy highlighted the importance of adopting clean energy technologies.
2008-2015: Cost of PV Cells Falls with module prices decreased by around 85%. The cost reduction along with government incentives increased solar adoption. Hence solar has become a mainstream source globally.
Present: Solar Panel Adoption in the US reflects the growing popularity and affordability as the latest sources confirm that millions of houses in the United States have solar panels installed.
Recent solar panel advancements include the development of Perovskite Solar Cells (PSC) – A promising technology that enhances efficiency and reduces manufacturing costs. Also, Floatovoltaics – The installation of solar panels on water surfaces, is another major innovation that focuses on space utilization and improves efficiency. Here are some of the other Latest Technologies in Solar:
- Solar Desalination which is used to desalinate seawater using solar energy, provides an endurable solution to water scarcity in dehydrated regions.
- Solar Trees are structures that have solar panels merged into their design, generating clean energy as well as delivering shade.
- Solar Cars use sunlight to generate electricity to run smoothly and reduce reliance on fuels.
Also, Solar is used in everyday items like Portable Solar Chargers, watches, cells, Solar-Powered Lights, Water Heaters, and Device charging Backpacks. These advancements and their practical application in life show us the expanding importance of solar energy.
Here is almost every information about History of Solar.
{Video Credit- edX}
The Future of Solar
The future of solar energy is overflowing with hopes fueled by Growth in the Solar Industry, Current Technological Advancements, Decline in Cost with more efficiency, and Expansion in the Industrial and Transport sectors.
We can witness Growth in the Solar Industry as the installations hold a high record in 2022, counting 2/3rd of all renewable energy. Due to the increasing demand and supporting government policies, the global solar energy market is anticipated to reach a whopping $370 billion by 2029. No doubt that solar will become the dominant source of electricity by the year 2050.
Researchers are working on the Current Technological Advancements to enhance efficiency using multi-junction designs to capture more sunlight and generate more electricity. The Battery Technology Advancements are under research to use sodium-ion that can deliver better sustainability and affordability. Also, it would be the best alternative to Liithium-ion batteries dominating the market.
In recent years, Solar panels have undergone an 80% Decline in Cost since 2010. With affordability, Solar power becomes more accessible for individuals, businesses, and even in other developing countries.
To attain more efficiency, Artificial intelligence (AI) is being used for optimizing the solar panel positioning, predicting energy production, and managing systems efficiently. Also, the Sun-tracking systems allow panels to adjust their position during the day, capturing sunlight at different angles and generating more energy.
Expansion in the Industrial and Transport Sector is observed as innovative solutions such as electric vehicles (EVs), solar carports, and integrated charging systems are emerging. There is a lot more to know about the future of solar energy eventually it will guide you take right decision regarding solar projects.
When was the first solar panel invented?
In 1881, the First solar panel was invented by Charles Fritts who put together the prototype using selenium. However, its efficiency was just a negligible 1%.
Further in 1954, Bell Labs revealed the game-changer – a silicon-based solar panel with 4% efficiency. Hence, this innovation created a path for the solar revolution that we are witnessing today.
When was the first solar house built?
To build the First Solar House early developers in the 1930s experimented with solar concepts. In 1948, this wedge-shaped wonder had south-facing panels and an innovative heating system.
However, the credit goes to earlier experiments like MIT’s 1939 Solar House, and the late 1940s became the turning point in solar housing. In 1944, Frank Lloyd Wright’s “Solar Hemicycle” blended passive solar design principles.
Ray is an avid reader and writer with over 25 years of experience serving various domestic and multinational private and public energy companies in the USA.