Bifacial solar panels are an advanced innovation in solar technology, capable of capturing sunlight from both sides of the panel, which is different from the traditional monofacial panels that are capable of capturing light from only one side. Hence, this unique design of bifacial solar panels made it easier to generate more electrical power with the same surface area compared to monofacial panels.
The concept of bifacial solar cells was discovered by the Soviet Space Program during the 1970s to maximize energy production. However, it took a few more years for bifacial panel technology to mature and gain acceptance in the solar industry.
Before you get to know the later parts whether Bifacial solar panels are worth it, Tariff Exemption, and Bifacial vs Monofacial Solar Panels, you must know other related concepts. It includes knowing what are Bifacial Solar Panels, its core structure, design, working, pros and cons. Also, we will walk you through various applications of bifacial solar panels and analyze whether it is suitable for residential use.
What are Bifacial Solar Panels?
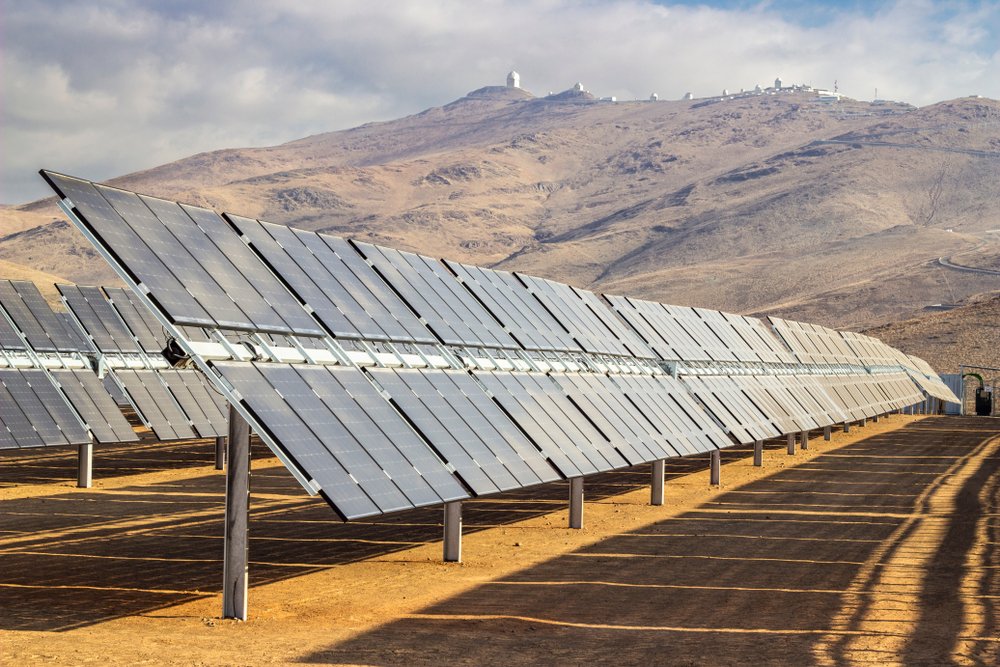

Generally, the Monofacial panels function by absorbing the sunlight with their top surface, and then converting it to electricity. However, Bifacial panels also absorb sunlight on the top, but in addition to that, they absorb light from the ground or surrounding environment which is reflected to the panel’s backside (also referred to as Albedo Radiation).
Although, different types of bifacial solar panels are available in the market, that includes using either Monocrystalline or Polycrystalline photovoltaic cells. However, many are using PERC (Passivated Emitter and Rear Cell) and also other advanced technology cell structures like PERT and Heterojunction. Besides this, there are also so many different types of solar panels.
Bifacial panels are most commonly used in large-scale ground-mounted solar farms and commercial rooftop installations. Especially where these panels can be positioned and aligned to improve the absorption of reflected light on the backside. Also, these Bifacial panels are ideally suitable for use in solar canopies, carports, and pergolas.
Structure and Design of Bifacial Solar Panels
The Bifacial solar panels are designed and constructed to capture sunlight from both sides, utilizing a transparent sheet at the backside or a double-sided glass frame. In this way, light is allowed to pass through the backside, reaching the photovoltaic cells.
Additionally, even the photovoltaic cells are designed double-sided so that they can maximize the panel’s absorption capability of the reflected light hitting the panel’s backside.
More preference is given to the transparent frame, mounting systems, junction box and wirings as they all are arranged in a unique pattern to minimize shading at the backside of these Bifacial solar panels.
How Do They Work?
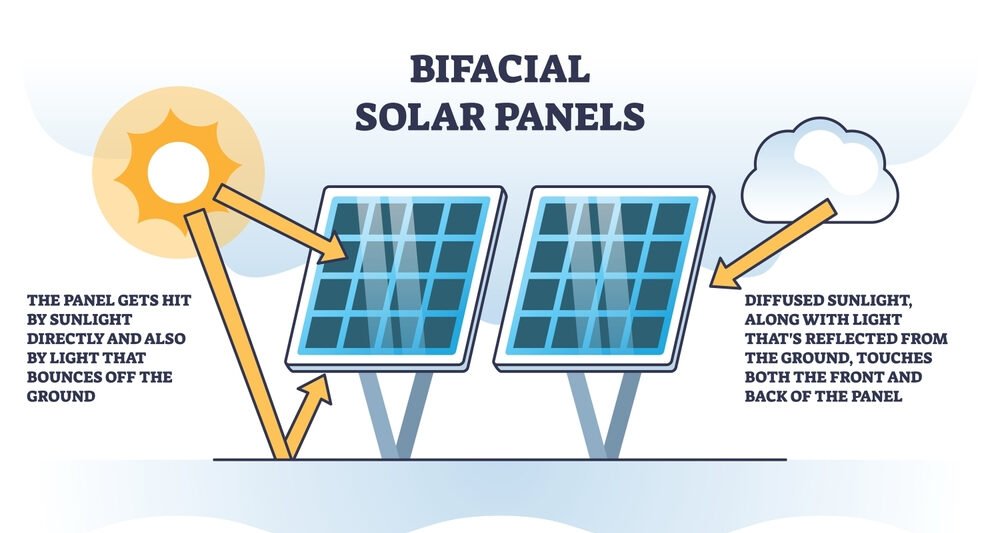
Here, Albedo plays a major role in enhancing these Bifacial panel efficiency and generates an additional amount of energy obtained from sunlight reflectivity on the panel’s backside. White TPO roofing membranes, snow, and sand have light-coloured, smooth coatings that are capable of reflecting even the smallest amount of light. As a result, it greatly boosts bifacial production, especially the panel tilt angle impacts how much light is reflected reaching the back. You should also know how all solar panels work.
Pros of Bifacial Solar Panels
Here are a few important benefits of bifacial solar panels that include:
- Increased energy yield: By capturing light from both sides, bifacial panels are capable of producing 10% to 30% more energy than monofacial panels within the same amount of space
- Potential for lower levelized cost of energy (LCOE): Bifacial panels have a costlier upfront, but their higher efficiency and energy yield can result in competitive costs on a $/kWh basis within system life. The ROI depends on Albedo, by which bifacial solar panels can attain 11% to 27% energy production in ground-mount systems.
- Improved performance in snowy or reflective environments: Snow reflects some additional light, which is an advantage for bifacial panels during winter, having a great performance boost compared to monofacial panels.
- Durable design and longer lifespan: Many bifacial panels utilize sturdy glass-on-glass designs, extending life up to 30+ years. Also, not using a back sheet can decrease degradation.
Cons of Bifacial Solar Panels
Despite advantages, these Bifacial Solar Panels come with a few disadvantages or drawbacks to be considered, including:
- Higher upfront cost: Bifacial panels are usually 10-20% costlier than monofacial panels because of their more complicated design and manufacturing.
- Increased complexity for system design and installation: Copying or Imitating the bifacial system’s estimated energy yield requires adjusting site-specific factors like — albedo, tilt, row spacing, specialized racking, and mounting hardware.
- Variable performance depending on site conditions: The Bifacial Panel’s energy gain varies from 5% to 30% based on the system design and environment. Soiling the backside can decrease bifacial output over a long time.
- Additional maintenance considerations: Bifacial panels will need frequent cleanings for better performance. Especially during dusty/snowy environments, some bifacial panel designs help minimize snow accumulation.
Applications of Bifacial Solar Panels
Currently, bifacial panels are very commonly used in large-scale ground-mounted solar farms. Their higher efficiency helps in maximizing land utilization and reducing overall costs. Tracking systems are often utilized to optimally adjust panel angles throughout the day.
These Bifacial panels are being utilized in many applications like — elevated solar canopies and carports, where it is valued more for their aesthetics and increased performance. Also, Agricultural solar arrays (agrivoltaics) use bifacial panels, allowing more sunlight to pass through to crops.
Are Bifacial Solar Panels Suitable for Residential Use?

- Ground-mounted residential arrays with sufficient spacing and reflective ground surface.
- Elevated solar structures such as — awnings, pergolas, and carports where reflected light can reach the panel’s backside.
- Poolside structures
House owners who typically consider buying bifacial panels must very carefully evaluate whether their house has the right environmental conditions. They must ensure taking advantage of the bifacial design. However, the upfront cost and long-term durability should be noted and compared to traditional monofacial panels.
Bifacial vs Monofacial Solar Panels
Here are some of the key considerations while comparing bifacial panels to monofacial:
| Factors | Bifacial Solar Panels | Monofacial Panels |
| Efficiency | Higher efficiency due to capturing sunlight on both sides of the panel.
15-20% (front) + 5-25% (back) |
Lower efficiency compared to bifacial panels.
15-22% |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Affordable compared to bifacial panels. |
| Material | Requires more raw materials for manufacturing. | Requires fewer raw materials compared to bifacial panels. |
| Installation Requirements | Can work at more angles and orientations. | Need to be installed at an angle between 30 and 45. |
| Installation Angle | Can work at more angles, including a 90-degree angle. | To be positioned at an angle between 30 and 45. |
| Durability | Designed to withstand various weather conditions | It is durable and handles different weather conditions |
| Maintenance | Regular clean-up is required to remove dust and dirt. | Regular maintenance has to be done to remove dust and dirt. |
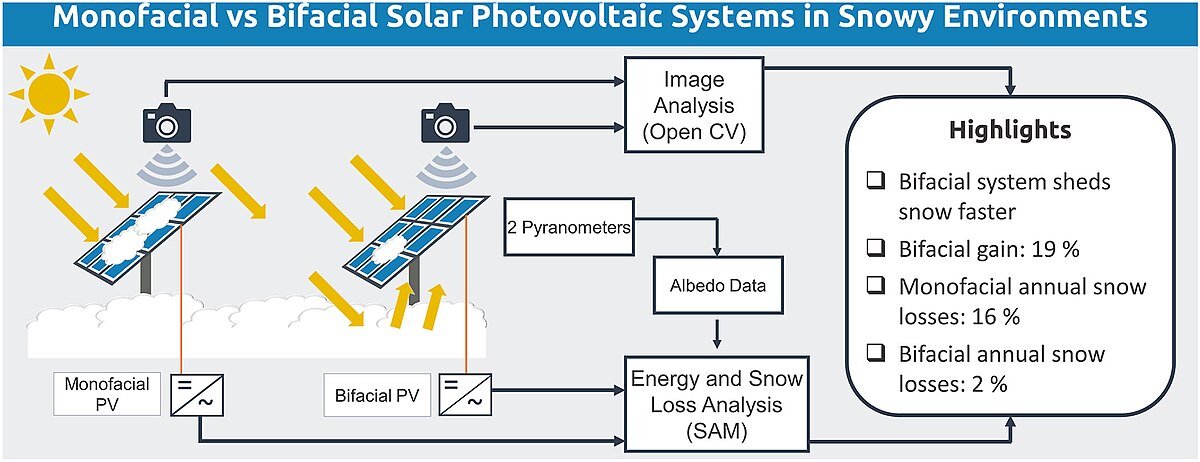
Here, you can see an example of how much bifacial solar panels are effective in comparison to monofacial solar panels in snowy environments:-
Tariff Exemption on Bifacial Solar Panels
Solar tariffs are the taxes or duties that are imposed on imported solar panels. Governments have implemented these tariffs to protect the nation’s solar manufacturers and bring growth in the domestic solar industry.
It was January 2018, when the Trump administration imposed tariffs on imported solar panels and solar cells, being a part of Section 201 which refers to safeguard measures. At that time, the tariffs were implemented at 30% and gradually reduced by 5% each year.
Here is a timeline of how bifacial solar panels were exempted, and then the tariffs were reimposed:
- June 2019: Bifacial solar panels received tariff exemption.
- October 2020: The Trump administration removed the exemption for bifacial panels, saying that it was against the principles of the Section 201 tariffs.
- November 2021: The U.S. Court of International Trade (CIT) granted the exemption for bifacial systems depending on legal rules and regulations, saying that they were not liable to the tariffs.
- January 14, 2022: The Biden administration filed an appeal for the exemption, asking to reactivate the tariffs on bifacial solar panels.
In response to the United States government, a few Chinese manufacturers have been avoiding the US import duties. They were exporting solar equipment and supplies from other Southeast Asian countries to the US. As a result, the US government has scheduled to impose on these companies from June 2024 as the new prohibitive import tariffs.
Are Bifacial solar panels worth it?
Bifacial solar panels can be suitable for those people whose applications and situations are as the following:
- Space availability: Bifacial panels are capable of producing electricity from both sides, which is advantageous in areas with huge space and reflective surfaces, like — open fields or light-coloured rooftop surfaces.
- Energy yield: These Bifacial panels generate 10% to 30% more electricity compared to traditional monofacial panels.
- Aesthetics: Having a slim and modern appearance, Bifacial Panels are most preferred for specific architectural or design points of view.
- Long-term investment: These bifacial panels have a higher upfront cost compared to monofacial panels, but high energy generation results in long-term returns on investment.
Also, while buying a Bifacial solar panel, one must keep these factors in mind that include — Cost, Site-specific conditions, Installation, mounting, System design and compatibility.
Ray is an avid reader and writer with over 25 years of experience serving various domestic and multinational private and public energy companies in the USA.

