Carbon footprint is the amount of greenhouse gas emissions like carbon dioxide (CO2) which is released into the atmosphere due to human activity.
Solar energy as a clean and renewable energy source is a perfect replacement for fossil fuels that helps reduce pollution by minimizing greenhouse gas emissions, improving air quality and preserving water resources.
The popularity of solar panels is surging in the US, having installed a total capacity of 161 GW solar panels at the end of December 2023. With the technological advancements, the cost of solar panels has significantly dropped over the past decade.
On the other side, if the manufacturing of solar panels isn’t clean, it causes air and water pollution. It is because the mining of rare earth metals and silicon production can emit greenhouse gases. However, the ongoing technological development plans for the best ways to increase the output of solar panels.
By the time you complete travelling throughout this article, you will know how to calculate the carbon footprint of solar panels that undergo three different lifecycles namely the upstream, operational and downstream processes. Also, you will gain knowledge about the various benefits of solar panel recycling that help to reduce the carbon footprint.
Calculating the Carbon Footprint of Solar Panels

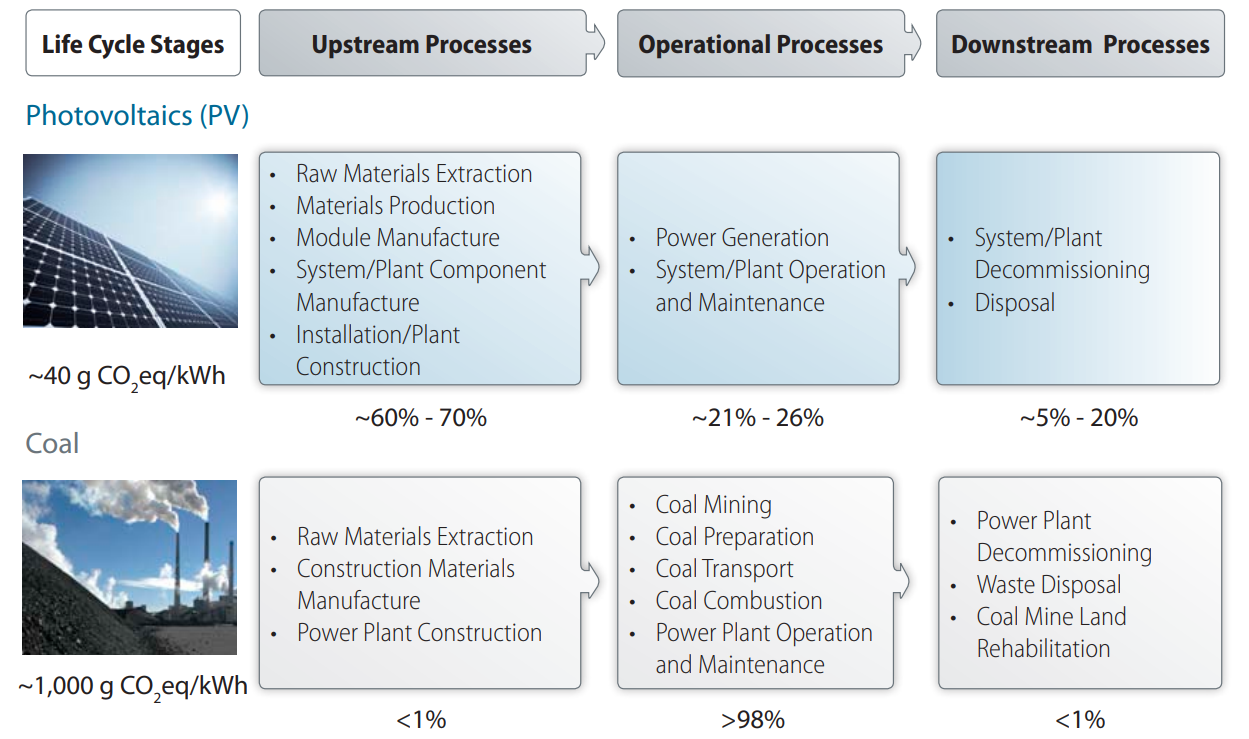
Based on the calculation of carbon footprint, a residential solar panel emits 40 grams of CO2 per kilowatt-hour of electricity generated. However, solar panels have a low carbon footprint, as they generate clean energy and offset emissions from fossil fuels, but their production and installation do involve some emissions.
There are three different stages of the life cycle of solar panels that produce diverse amounts of CO2 in each stage:
1. Upstream processes: These processes emit 60 to 70% of CO2 in each stage:
- Raw materials extraction and production
- Module Manufacture
- System or Plant Component manufacture
- Installation or Plant Construction
2. Operational processes: The Plant operation and maintenance process emits 21 to 26% of CO2 in each stage.
3. Downstream processes: The plant decommissioning and disposal process emits 5 to 20% of CO2 in each stage.
Each stage presents chances to reduce the carbon footprint of solar panels.
1. Upstream Process
The upstream process involves the extraction of these raw materials to make solar panels, which include:
- Silicon
- Glass
- Aluminium
- Silver
- Copper
- Tin
- Arsenic
- Semiconductor materials like cadmium telluride (CdTe) or copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS)
- Rare earth materials like indium, gallium, and selenium
Mainly, the photovoltaic systems emit greenhouse gases during the manufacturing process rather than during the operation. While manufacturing solar panels, significant energy inputs are required in the form of electricity and undergo chemical processes that emit CO2 gases and other pollutants, which can harm the environment if it isn’t properly treated. This is because the energy used in the production process involves the sources from fossil fuels. Typically, solar panels produce 50g of CO2 during manufacturing.
Especially, the transportation process for long distances requires fuel consumption and emits CO2 from vehicles, which depends upon various factors like the distance travelled and mode of transportation used.
Solar panels create pollution and affect the environment by using large areas for installation, which can lead to habitat loss and wildlife disruption. Furthermore, concentrated solar power (CSP) plants, consume a large amount of water for cooling, thereby depleting the available water resources and causing a scarcity in arid regions. Particularly, when solar panels reach their end of lifespan, proper disposal and recycling methods are required, and improper waste management systems can result in the release of hazardous materials into the environment.
2. Operational Process
Solar panels and solar power plants don’t produce CO2 while operating. Despite, being a clean and renewable energy source by generating electricity from the sun’s rays, some amount of CO2 is emitted during the manufacturing and transportation process as well as decommissioning solar plants at the end of their lifespan. Also, the installation process uses machinery which depends on fossil fuels. Various ongoing maintenance activities such as cleaning and repairs might consume additional energy and generate CO2 by maintaining lesser lifecycle emissions compared to fossil fuels.
3. Downstream process
The downstream process includes the disposal and decommissioning process of solar panels and plants, which can lead to negative environmental impacts and CO2 emissions due to inappropriate methods such as:
1. Ineffective Landfilling: Solar panels that contain materials like glass, plastic, and metals undergo degradation in the absence of oxygen that is found in landfills. When these materials are decomposed, gases like CO2 and methane (CH4) contribute to climate change. Especially, methane has a higher global warming potential than CO2 within a shorter time.
2. Incineration: When the solar panels are burnt without proper controls, it is known as the incineration process that releases CO2 and other gases into the atmosphere.
3. Inadequate recycling: The recycling process needs to be improved, and the inadequate facilities make it challenging to separate and recover valuable materials like silicon, metals, and glass. If these materials are lost, once again the additional extraction process continues which leads to higher CO2 emissions.
4. Incomplete dismantling: Materials like aluminium, glass, and copper are left behind due to the incomplete dismantling and decommissioning of solar panels. As a result, it causes land pollution and harms the wildlife. Most often, this type of issue occurs due to a lack of precise regulations and a lack of decommissioning activities that lead to emissions from equipment operation, transportation, and disposal.
How is It Possible to Reduce the Carbon Footprint of Solar Panels?
Reducing the carbon footprint of solar panels requires a broad approach across various stages such as production, transportation, consumption, waste management, policy, and regulations. In other words, these stages can help reduce carbon emissions by following a cleaner manufacturing process, increasing solar panel output and solar panel recycling. It helps to save lives, relieve the burden of the healthcare system and minimize wildfires.

Cleaner Manufacturing Process
Despite solar energy being a cleaner energy source, the PV panels emit a maximum amount of CO2 of 50 grams during the manufacturing process. You can learn about how solar panels are made in the present to get a better idea. However, several steps can be taken to implement cleaner manufacturing processes such as:
- Practising various energy efficiency technologies like upgrading machinery and equipment, optimizing heating and cooling systems and minimizing energy losses.
- Water efficient technologies and minimizing consumption can reduce the environmental impact of water extraction, treatment, and disposal.
- Implementing a closed-loop system can help the waste heat can power another energy system, thereby minimizing energy loss and raw material extraction.
- Using eco-friendly and non-toxic chemicals in the manufacturing process by removing the requirement of cadmium and ensuring to maintain the maximum efficiency.
- Reducing transportation distances for raw materials through regional supply chains can reduce the carbon footprint linked with material transport.
Many governments are encouraging companies to implement sustainable strategies by introducing various subsidies and tax breaks, such as the Investment Tax Credit (ITC).
Similarly, solar companies have taken initiatives to reduce hazardous wastes by implementing safer alternatives like gallium arsenide and copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS) as well as work on the development of various technological advancements for material reuse and recycling.
Increasing Solar Panel Output
There are several ways to increase the solar panel output and minimize the carbon footprint, such as:
- High-efficiency solar panels with ratings of 20% and above have a higher conversion capacity and maximize the output per meter square of the panel area.
- Orienting the solar panels by tilting towards the sun ensures optimal exposure. Also, choose panels from manufacturers following sustainable practices like using recycled materials and renewable energy in production.
- Ensure regular maintenance and cleaning as well as avoiding shading issues to maintain peak performance.
- Use high-efficiency inverters to convert DC to AC electricity with minimal energy losses.
- Integrate energy storage systems like batteries to capture and store excess energy during peak production periods.
However, you can get a rough idea of average solar panel output by reading: “How Much Power Does A Solar Panel Produce?“
Solar Panel Recycling
There are several benefits of recycling solar panels addressing environmental issues and conservation of resources which results in sustainable growth of energy such as:
- Recovering valuable materials like silicon, silver, copper, and aluminium reduces the extraction and destructive mining process.
- The overall carbon footprint of the solar industry can be reduced through recycling, as manufacturing requires significant energy input.
- Various economic opportunities are created by establishing many new industries and job markets that focus on the collection, dismantling, processing, and reclaiming of materials. Moreover, the sustainability of technologies can be ensured when the recycled materials are sold or reused by various industries.
- The long-term financial viability of the solar industry can be ensured by reducing the risks of waste accumulation and environmental degradation.
- Investing in solar panel recycling, the research and department focuses on technological advancements in waste management systems, material recovery and recycling processes.
How Can Going Solar Reduce Your Carbon Footprint?
By preferring solar energy you can reduce the carbon footprint which is indeed much lower than fossil fuels. Solar panels generate carbon emissions and other greenhouse gases only during the manufacturing process by generating 40 to 50 grams of CO2 per kWh of electricity generated in the first year and don’t cause any pollution during their operation. Whereas fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas release greenhouse gases during the extraction, transportation and combustion process. It is estimated that burning fossil fuels produces 34 billion tonnes (Gt) per year (Coal- 45%, oil- 35% and gas- 20%).
However, both solar energy and fossil fuels have an impact on the environment. Typically, solar panels contain toxic materials like lead and cadmium which become challenging to recycle and occupy large land areas, disturbing the wildlife habitat and ecosystem. Particularly, fossil fuels when they are burnt release harmful pollutants like nitrogen oxides, sulphur oxides, and particulate matter which reduce air quality, contaminate water due to oil spills and cause respiratory diseases.
Finally, solar energy as a clean, renewable, and infinite energy source is much better in the long run when compared to fossil fuels as it doesn’t deplete natural resources.
Ray is an avid reader and writer with over 25 years of experience serving various domestic and multinational private and public energy companies in the USA.

