Solar energy is an environmentally friendly source of energy, utilizing solar panels converts the sun’s energy into electric energy. Solar power is an important aspect of renewable energy that minimizes greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, decreases reliance on fossil fuels, and leads to a healthier future.
These solar panel technologies are developed to obtain electric power from sunlight through the Photovoltaic effect. These technologies play a major role in solar energy utilization for many purposes like — electricity generation, consumer electronics, and in remote areas where central power grid connection is challenging.
Although, there are various types of solar panels, of which 2 main categories are — thin-film solar panels and crystalline silicon solar panels.
To decide which solar panel is best for you amongst the thin-film and crystalline silicon solar panels, you must have an overview of these solar panels. However, throughout this article, we will keep you equipped with their advantages and disadvantages, comparing their efficiency, cost, lifespan, durability, performance under various conditions, applications, and appearance.
What are Thin-Film Solar Panels?

These thin-film solar panels are produced by utilizing different materials, of which here are the 4 most commonly used materials:
1. Amorphous silicon (a-Si): The a-Si type thin-film solar cell is composed of non-crystalline silicon, which is well-known for its low cost and durability.
2. Cadmium telluride (CdTe): The CdTe type of thin-film solar cells are created from a thin layer of cadmium telluride, recognized for its high absorption coefficient and low-cost production.
3. Copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS): CIGS type of thin-film solar cells comprise a thin layer of copper indium gallium selenide that has a high-efficiency potential.
4. Organic photovoltaic (OPV) cells: OPV type of thin-film solar cells are comprised of organic materials like polymers or small molecules, which are known for their flexibility and low production cost.
Thin-film solar panels are being utilized in a variety of applications like Building-Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV), which embeds solar panels inside building materials such as — windows, roofs, or exterior walls. Also, they are frequently utilized in portable applications (like solar chargers) and large-scale solar power plants.
Advantages of Thin Film Solar Panels
Thin-film solar panels come with a lot of advantages compared to crystalline silicon solar panels. Some key advantages include:
- Flexibility and Portability: Thin-film solar panels are lightweight and flexible, in applications where rigid solar panels are not possible. They can be moulded into curved surfaces or can even be used in portable devices.
- Low-cost production: The cost of production is low for Thin-film solar panels when compared to crystalline silicon solar panels. Also, the manufacturing process is not complicated and requires less material.
- Lightweight: Thin-film solar panels are much lighter than crystalline silicon solar panels, making them much simpler to handle and install. Also, these Thin-film solar panels are beneficial in places where weight is a concern, such as — rooftops or portable applications.
- Higher shade tolerance: Thin-film solar panels have higher shade tolerance than crystalline silicon solar panels, allowing them to produce electricity even in partially shaded conditions.
Disadvantages of Thin-Film Solar Panels
Despite their remarkable advantages, thin-film solar panels also come with a few disadvantages, including:
- Lower efficiency: Thin-film solar panels operate at lower efficiency compared to crystalline silicon solar panels. Whereas, a few thin-film technologies are capable of achieving higher efficiencies. However, thin-film solar panels averagely have lower conversion efficiencies than crystalline silicon solar panels.
- Shorter lifespan: Thin-film solar panels naturally have a shorter lifespan of just 20–25 years compared to crystalline silicon solar panels which last up to 30–35 years.
- Temperature sensitivity: Thin-film solar panels are very sensitive to temperature changes compared to crystalline silicon solar panels and due to this, High temperature decreases performance, and low temperature affects efficiency.
What are Crystalline Silicon Solar Panels (c-Si)?
At present, Crystalline silicon solar panels are the most widely used type of solar panels. These panels comprise silicon atoms bonded together to form a crystal lattice structure. Hence, this well-organized structure helps to make an efficient conversion of light into electricity.
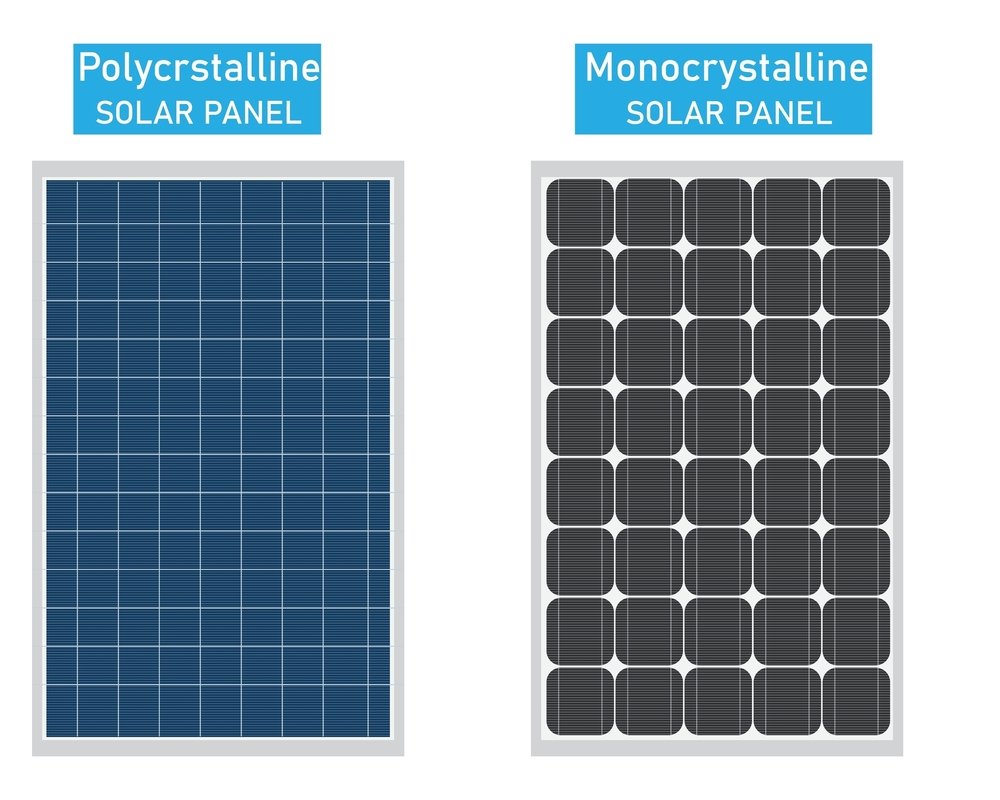
Here are the 2 main types of crystalline silicon solar panels:
Monocrystalline silicon (mono c-Si) is obtained from a single crystal structure. These panels have an evenly distributed structure and a high efficiency. Monocrystalline silicon solar panels are well known for their black or dark blue colour.
Polycrystalline silicon (poly c-Si) is formed from a lot of silicon crystals. These panels have a mixed appearance and a little lower efficiency compared to monocrystalline silicon solar panels. Polycrystalline silicon solar panels are known for being mostly blue.
Crystalline silicon solar panels are produced from silicon wafers as the base material, which are further processed and chemically treated to achieve the required electrical properties. The manufacturing process of crystalline silicon solar panels is much more complicated compared to thin-film solar panels.
There is a wide range of Crystalline silicon solar panel applications, of which they are mostly utilized in residential and commercial solar installations. Also, these crystalline silicon solar panels are used in large-scale solar power plants and many off-grid applications, like — supplying power to remote buildings or generating electricity in rural areas. However, if you want to install crystalline solar panels, you should know which panel will be best for you- polycrystalline or monocrystalline.
Advantages of Crystalline Silicon Solar Panels
Crystalline silicon solar panels deliver many advantages compared to thin-film solar panels, and here are some of the major advantages that include:
- More efficiency: Crystalline silicon solar panels usually have higher conversion efficiencies than thin-film solar panels. Whereas, Monocrystalline silicon solar panels operate at much higher efficiencies compared to polycrystalline silicon solar panels.
- Durability and long lifespan: Crystalline silicon solar panels are popular for their excellent durability and long lifespan, which are capable of lasting up to 30–35 years. Even after that lifespan, these crystalline silicon solar panels tend to produce greater than 80% of their original power.
- Lower Temperature Coefficient: Crystalline silicon solar panels have a lower temperature coefficient compared to thin-film solar panels. Therefore, these panels are less affected by high temperatures. Although, it will lose its performance slightly only when it gets too hot.
Disadvantages of Crystalline Silicon Solar Panels
Despite having good advantages, these crystalline silicon solar panels also come with a few disadvantages, such as :
- Cost and Energy-Intensive Production: The production of crystalline silicon solar panels is extremely energy-intensive and costly as compared to thin-film solar panels. Also, its manufacturing process demands more material and uses a more complicated process.
- Heavy and Rigid: Crystalline silicon solar panels are much heavier and rigid compared to thin-film solar panels. As a result, it becomes difficult to handle and install these panels. Especially in specific cases where weight and flexibility are important factors.
- More Space Required: Crystalline silicon solar panels require more space for installation as compared to thin-film solar panels. Despite having high efficiency, these crystalline silicon solar panels demand a bigger area to generate the same amount of electricity, which can be a limiting factor in some installations.
The Difference between Thin-film and Crystalline Silicon Solar Panels: Which is right for you?
Here is a detailed comparison of thin-film solar panels vs crystalline silicon solar panels:
| Feature | Thin Film Solar Cells | Crystalline Silicon Solar Cells |
| Efficiency | Low | High |
| Cost | Low | High |
| Durability and Lifespan | Short | Long |
| Performance under various conditions | Best in low light and high temperature | Best in high light and low temperature |
| Application | BIPV and Portable Devices | Large-scale solar farms and Residential Rooftops |
| Appearance | Flexible structure with various colours | Rigid structure with Black or Blue colour |
Also, remember that while comparing thin-film and crystalline silicon solar panels, there are a few factors that have to be closely considered. To determine which solar panel is the right choice for you is based on factors like — Efficiency, Cost, Durability and Lifespan, Performance under various conditions, Application, and Appearance.
Efficiency
Crystalline silicon panels, which include both types — monocrystalline and polycrystalline, operate at higher efficiencies ranging from 15% to 25%.
Whereas, the efficiency of thin-film panels will vary based on the type of photovoltaic material used in the panels. Hence, these thin-film panels have efficiencies ranging between 7% and 18% which is less compared to crystalline silicon panels.
Despite this, many consumers are expecting thin-film panels to become much better than crystalline silicon panels in the future because of the continuing technological improvements being made in thin-film solar panels to make them more efficient. There is also lot more to know about solar panel efficiency.
Cost
The production costs of crystalline silicon panels are relatively higher compared to thin-film panels. Whereas, due to thin film panels’ lower efficiency, more panels will be needed to supply the same volume of power compared to the monocrystalline panels.
As a result, it will increase the total cost, specifically for large-scale installations. However, the choice of selection between these technologies will vary depending on the respective application requirements and budget.
Durability and Lifespan
Compared to crystalline silicon solar panels, Thin-film solar panels are more prone to degradation due to lower durability and lifespan.
Crystalline silicon solar panels are widely recognized for their excellent durability and long lifespan, which usually lasts up to 30–35 years.
In comparison, thin-film solar panels have a shorter lifespan, lasting 20–25 years. However, both types of panel lifespan can be affected based on various conditions like — weather, temperature, and installation.
However, proper installation and maintenance are very important, which leads to a longer lifespan.
Performance under various conditions
Thin-film solar panels are equipped with better temperature coefficients compared to crystalline silicon-based panels. Hence, these thin-film panels have a lesser impact during high temperatures. However, it will slightly degrade in performance, but only when it gets too hot and this affects their suitability for different geographic locations.
Application
Thin-film solar panels are most suitable for applications like BIPV (Building-Integrated photovoltaics) because of their slim and flexible nature. Also, they are the best suitable for many portable applications.
Whereas, crystalline silicon panels are considered the preferred choice compared to thin-film solar panels, mostly used for large-scale and permanently fixed installations because of their higher efficiency and durability.
Appearance
Thin-film solar panels can be either blue or black based on the photovoltaic material that was utilized to create them. As these panels are flexible and thin in structure, they are capable of providing aesthetically attractive designs and advantages in various applications.
On the other hand, Crystalline silicon panels are very rigid and have a unique appearance, which could be more or less appealing based on aesthetic preference and specific applications.
Conclusion
The choice between thin-film and crystalline silicon solar panels varies depending on project-specific requirements, budget, and installation requirements. Thin-film solar panels come with many benefits in terms of flexibility, cost, and low-light performance.
Meanwhile, crystalline silicon solar panels are superior in efficiency, durability, and long-term cost-effectiveness. By understanding the unique features and applications of both these technologies, proper decisions can be made to take advantage of the solar energy benefits.
Ray is an avid reader and writer with over 25 years of experience serving various domestic and multinational private and public energy companies in the USA.

