Solar panels are defined as technologies that help to transform the sun’s energy into electric current by way of the photovoltaic effect. Photons from sunlight push electrons into a more powerful form of energy, thereby generating a supply of electricity.
The benefits of Solar panels tend to include renewable energy production and distribution, savings on electricity bills, low maintenance expenses, and environmental protection by decreasing the dependency on fossil fuels.
Over the years, Solar panel efficiency has gradually got better due to technological advances and manufacturing processes, with newly developed panels attaining more than 20% efficiencies.
The manufacturing process of solar panels has greatly advanced through the use of automation, enhancements in the material’s efficiency, and research into new means of production. These include thin-film solar cells and bifacial panels, the best alternatives to silicon solar cells.
Though it is essential to know how solar panels are made, it is equally crucial to understand what solar panels are made of and where is it made. Did you know why popular solar companies JinkoSolar, Trina Solar, and Canadian Solar are made in China?
Let us further explore why newly manufactured Solar Panels are tested and factors like Quality Assurance, Performance Verification, Reliability, and Customer Satisfaction. Also, there have been many questions arising about whether Solar Manufacturing is bad for the Environment or whether it is possible to make your solar panels. By the time you have completed reading, you will find the answers to these queries within this article.
What are Solar Panels Made of?
Solar panels are most commonly made of materials like silicon transistors, heat-resistant glass, metal components, and encapsulated materials such as EVA (ethylene vinyl acetate).
The most important part of solar panels is the silicon wafers, the semiconductors that form the solar cells, as they efficiently convert the radiation from the sun into electrical energy.
Different types of solar panels consist of monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film solar panels. Each with a variety of cell structures impacts price and efficiency, as Monocrystalline panels are known to be very expensive but more efficient. Whereas. Polycrystalline and thin-film panels are more economical but generally less efficient.
How are Solar Panels Made?

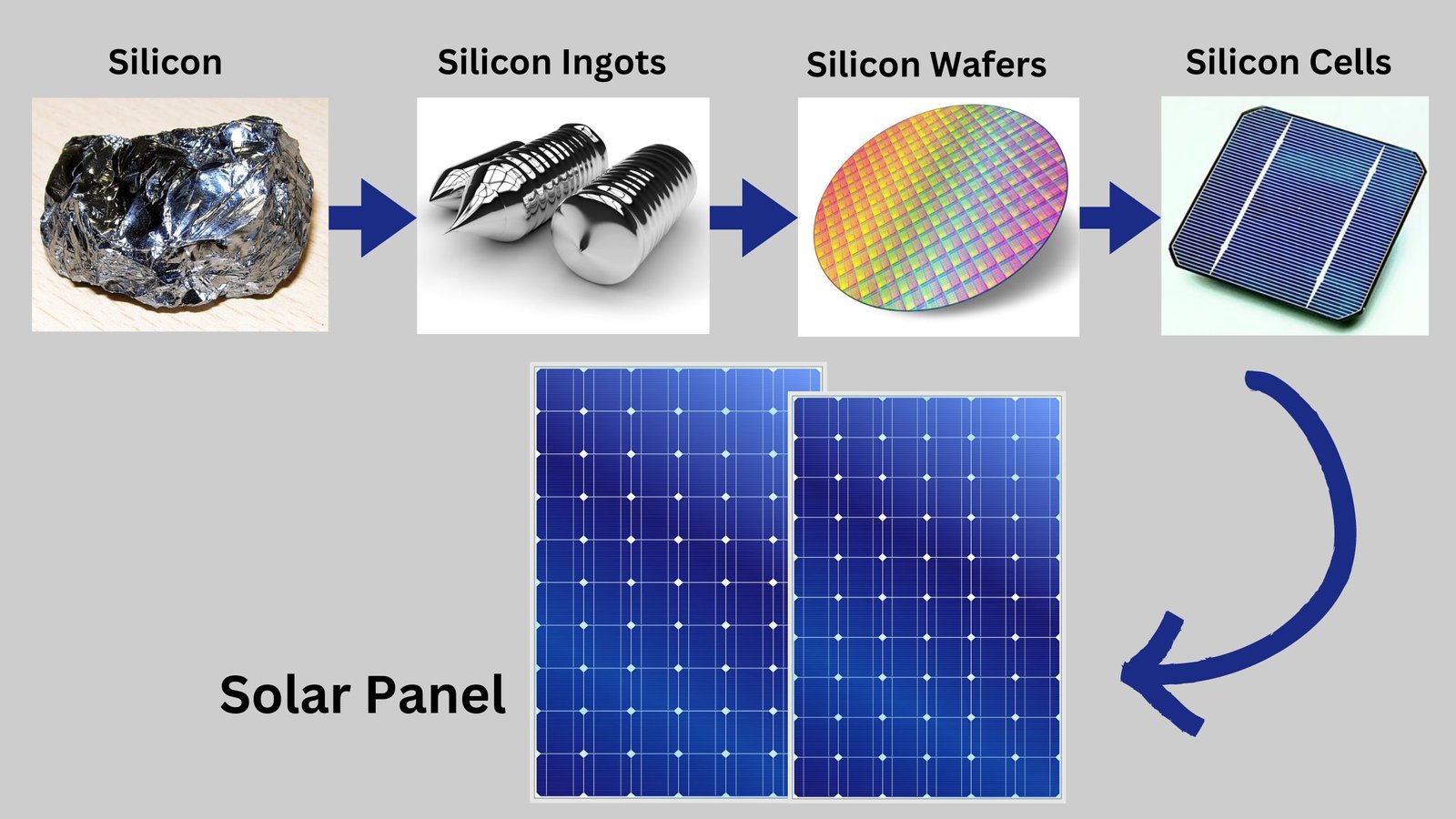
Solar panels, also referred to as photovoltaic (PV) panels, are built through a multi-stage manufacturing process that involves the processing of raw materials. It is further transformed into usable solar cells, which are then put together into panels ready for use.
1. Silicon Ingot Production: The process begins with, obtained from 100% pure silicon, which is melted in a furnace for heating and then converted into solid ingots through a method called the Czochralski process or the float-zone method.
2. Wafer Slicing: The silicon ingots are chopped into thin wafers (200 micrometres thickness) using specialized cutting tools.
3. Wafer Surface Treatment: The silicon wafer surfaces are chemically processed to get rid of impurities and harmful substances.
4. Doping: A process of applying impure substances into the silicon wafers to produce regions with different electrical properties.
- Phosphorus is used to produce excess electrons (n-type doping).
- Boron is used to create a low amount of electrons (p-type doping).
5. Solar Cell Fabrication: The doped silicon wafers are then put through a set of photolithography and chemical vapour deposition processes to form the various layers that are required for solar cell operation. This includes the deposition of
- Metal contacts
- Anti-reflective coatings
- Grid pattern application, speeding electron flow.
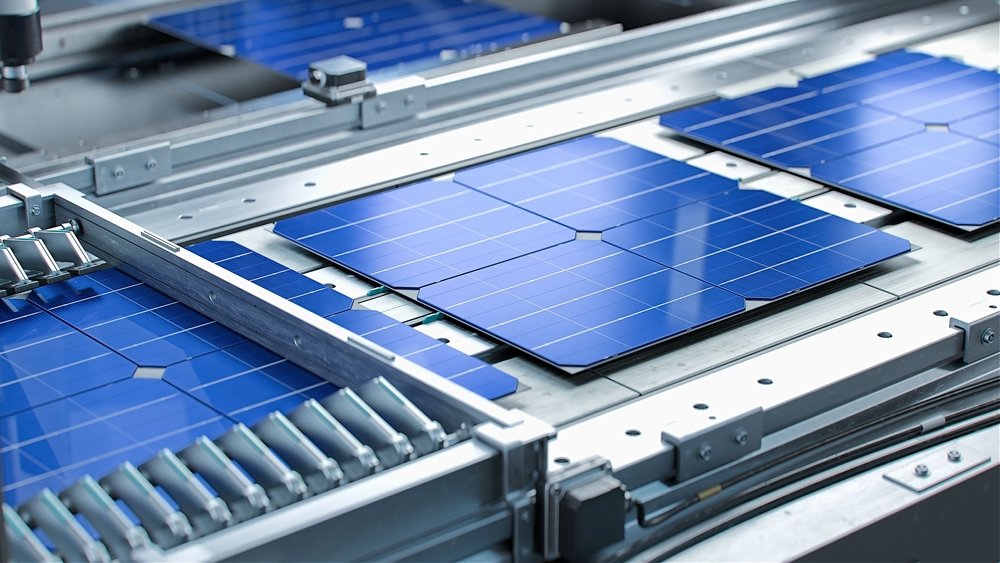
6. Testing and Sorting: As soon as the solar cells are designed and manufactured, they undergo thorough testing to make sure that their efficiency and performance match the expected standards.
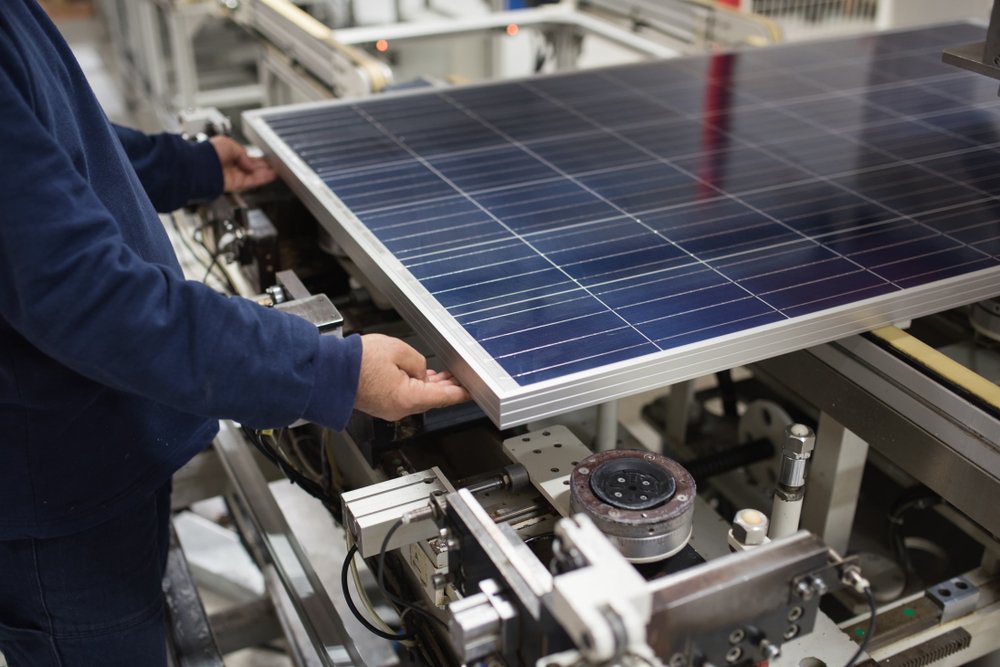
7. Panel Assembly: Solar cells are linked together and coated within a shield layer to create a solar panel. In most cases, many solar cells are connected using electrically conductive tape or wrapping wires to achieve the desired voltage and current output.
8. Encapsulation: The paired solar cells are tightly enclosed between layers of glass or plastic to protect them from harmful environmental factors such as water and mechanical damage to enhance solar panel durability and longevity.
9. Frame Attachment: The Frames made of metal such as aluminium or other metals are connected to the protective solar cells to give structural support and speed up the installation process.
10. Quality Control and Testing: Each manufactured solar panel goes through quality control checks and testing to verify that it satisfies industry standards for performance, durability, and safety.
11. Packaging and Distribution: After the solar panels successfully pass quality inspection tests, they are carefully packaged and made ready for distribution to consumers or installation locations.
By following the above steps, companies can build high-quality solar panels that are capable of turning sunlight into electric energy effectively and efficiently.
Where are Solar Panels Made?
Solar panels are mostly manufactured in Asian countries, particularly China, due to lower labour costs and access to raw materials like silicon.
A few less expensive solar brands are manufactured in China, namely — JinkoSolar, Trina Solar, and Canadian Solar.
Popular US production companies that manufacture top-notch quality solar panels are First Solar, SunPower Corporation, and Tesla (formerly known as SolarCity).
How are newly manufactured Solar Panels tested?

Solar panels undergo many performance tests to measure their electrical output under Sun Simulator, including analyzing parameters like — voltage, current, and power output to make sure that they meet minimum efficiency standards.
However, this test is useful to look for any possible product weaknesses or manufacturing defects ensuring long-term reliability, especially in humid areas.
These solar panel tests are very important as they help to determine:
- Quality Assurance
- Performance Verification
- Reliability
- Customer Satisfaction
Therefore, the in-depth testing of brand-new manufactured solar panels is necessary to confirm solar energy’s technological development and widespread application. You can learn more about solar panel testing and certifiction.
Is Solar Manufacturing Bad for the Environment?
In some cases, Solar manufacturing might have adverse environmental impacts like — energy consumption, raw material extraction, and chemical usage. However, solar energy’s overall positive environmental benefits are greater than fossil fuels, particularly industries that are advancing towards healthier and more sustainable methods of production.
The lifetime carbon footprint of a solar panel is:
- Manufacturing
- Operation
- Removal and Disposal
However, they are much lower than that of fossil fuels because modern panels eliminate a carbon footprint within 1–4 years of operation.
There are a few Environmental Benefits of solar panels, such as
- Reduced Greenhouse gas emissions (GHG)
- Air pollution
- Dependencies on fossil fuels
- Environmental well-being
- Tackling climate change
However, Companies are attempting to reduce solar manufacturing’s impact on the environment through recycling programs, reducing energy consumption, and developing more sustainable materials and production processes.
Can you make your own solar panels?
Yes, It is technically possible, but making DIY solar panels is challenging and potentially dangerous for non-professionals because of the manufacturing complexity, risk factors, and lack of energy efficiency and reliability.
Generally, DIY solar panels are homemade panels that are constructed from a variety of materials, at times with lower efficiency and reliability in comparison to industrially manufactured panels.
DIY solar panels do not come with warranties, certifications, and quality control. However, it not only leads to performance issues but also creates a high-risk and harmful environmental impact on the surroundings. Hence, it is not at all eligible for government incentives or the grid connection because of the hazardous characteristics that it possesses.
Ray is an avid reader and writer with over 25 years of experience serving various domestic and multinational private and public energy companies in the USA.

