Solar energy is the radiant UV light harnessed by the sun, using PV (Photovoltaic) cells to capture and convert it into electricity.
As of 2023, the global market for solar energy is said to have accounted for around 15% of energy production, compared to 4.2% in 2012. However, after 2010, the average cost of solar panels has gradually decreased, making them accessible to many, which is another factor for its growing popularity.
The main categories of PV Installations include residential, commercial, and utility-scale systems (which also include community solar under this). And, each of these categories has its unique purposes and characteristics, providing different energy needs and environments.
Let’s explore the three main types of solar projects: residential, commercial, and utility-scale systems, and the differences between them. These are essential in determining the right type of solar project for your specific needs and circumstances.
Residential Solar
Solar system installation in homes is referred to as residential solar, which involves using solar panels, inverters, and battery storage. Further, the inverter transforms the obtained DC (Direct Current) into AC (Alternating Current) electricity, which is most often used for household appliances. Either the homeowners can use the converted electricity directly store it in a battery for later use, or even sell the excess power by sending it back to the grid via net metering plans.
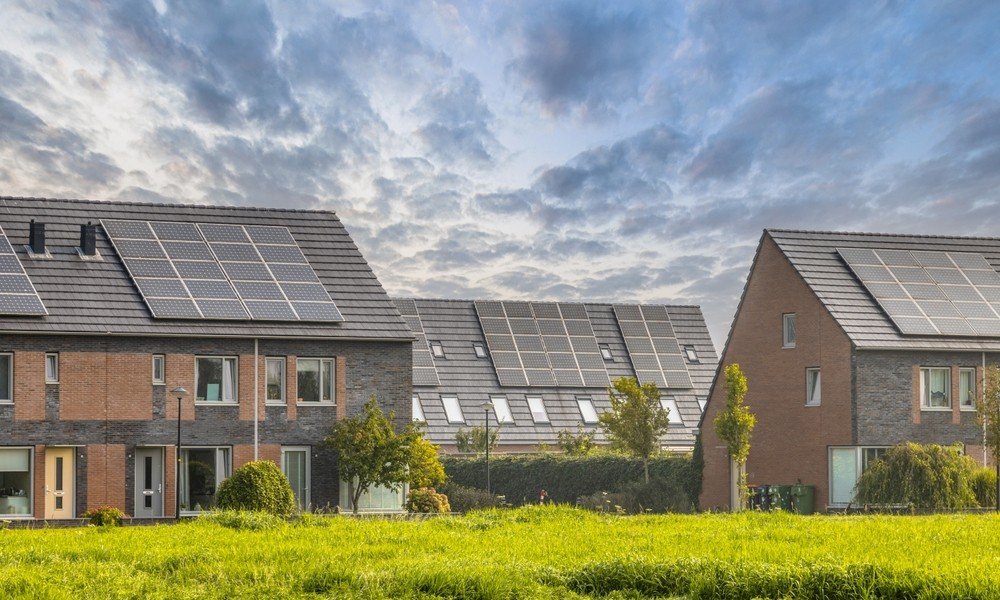

Typical placement of residential solar installations is on rooftops, which allows for capturing plenty of sunlight without occupying additional land space. The scale of residential solar installations differs, ranging from 3 kW to 10 kW for an average home (depending on energy usage and roof size). When it comes to choosing rooftop vs ground-mount installations, there are cost and efficiency implications for both.
Rooftop installations are usually less expensive and use existing building materials. Whereas, ground-mounted systems are often efficient as they have good exposure to the sun and can adjust panel angles. However, ground-mounted systems demand more space and might be restricted by zoning regulations.
However, installing solar arrays can be beneficial to residential homeowners as it reduces electricity bills, increases property value, and helps qualify for tax incentives or rebates.
Despite coming with many benefits, the challenges of residential solar result in higher initial costs. However, there are other ways to eliminate that cost with many financing options and incentives.
Sometimes, the homeowners might face issues regarding the roof suitability, which include orientation, shading, local regulations, and time-to-time maintenance. In addition, the solar panel efficiency can be impacted by weather conditions and geographic location.
Commercial Solar
Solar system installations in business properties are referred to as commercial solar systems, which consist of solar panels, inverters, and other necessary equipment to convert sunlight into usable electricity. These systems often differ in complexity and size, and range from small rooftop installations to large ground-mounted solar farms. Hence, these systems are intended to reduce energy costs, result in energy independence, and further contribute to the sustainability of renewable energy sources.
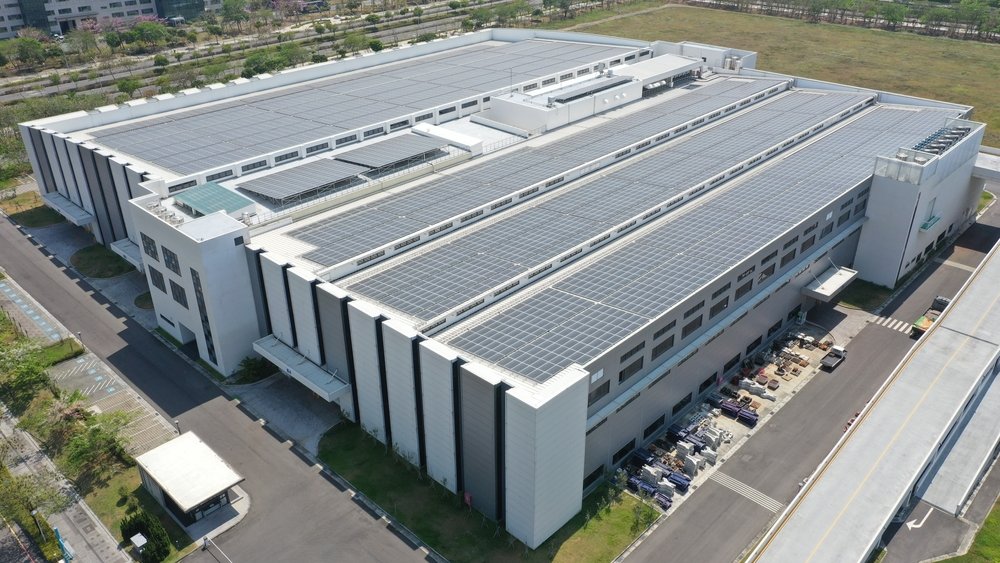

Applications of Commercial solar systems in various business settings include:
- Retail Stores: Most of the retail business stores have opted to install solar panels on their rooftops. In particular, the large stores that have high energy consumption use commercial solar systems to minimize energy costs.
- Manufacturing factories: To power the machinery and lower the operating cost, most of the large factories use commercial solar systems, especially helpful to energy-intensive industries.
- Business Buildings: Many corporate offices benefit from solar installations as they help to lower electricity bills and enhance sustainability, making them attractive to environment-conscious employees.
- Agricultural Service and operation: One of the most beneficial aspects is many farmers benefit from commercial solar systems for irrigation systems, heating, and cooling, as it reduces dependency on fossil fuels and lowers operational costs.
The advantages of adopting solar power for commercial use are:
- Cost Savings after the initial investment price are offset.
- Tax Incentives cover a part of the installation cost for businesses.
- The company’s sustainability and building brand image to attract customers.
- Businesses gain energy independence and stay protected from fluctuating energy prices.
Despite many benefits, businesses face a few challenges in adopting solar power, such as:
- Higher Initial Costs
- Space Limitations
- Regulatory Disputes
- Maintenance and Reliability
Utility-Scale Solar
Solar farms that implement large-scale solar energy installations are referred to as Utility-scale solar projects. Also, it generates and sells electricity to utilities or other large consumers, as it has a capacity of 20 MW (megawatts) or more. And, this capacity is more than sufficient to power up thousands of homes or industrial factories. Using PV panels (photovoltaic) or CSP (concentrated solar power), tends to produce energy on a large scale.
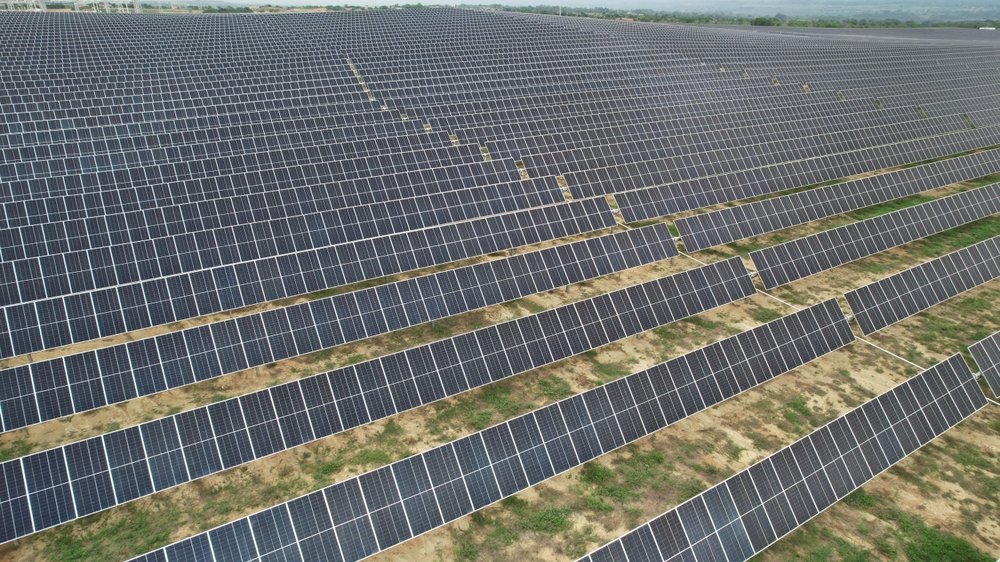

Typical buyers of these large-scale solar projects are electric utilities, who are buying the generated electricity to supply it to their customers. Also, the other buyers could be large corporations who are looking to meet sustainability or reduce their energy costs. In addition, these buyers usually decide to tie up themselves with a long-term PPA (power purchase agreement) to maintain stable pricing and a regular supply of renewable energy.
The sizes can vary in utility-scale solar projects, as most of the installations exceed 100 MW (megawatts). And, the highest scope of the largest solar farms could reach capacities of many hundred megawatts, which would typically cover plenty of land areas.
The benefits of Utility-scale solar projects are:
- Cost Efficiency leads to lower costs per megawatt compared to smaller installations.
- Grid Stability helps reduce dependency on fossil fuels.
- Reduction in Environmental Impact by eliminating greenhouse gas emissions and other pollutants.
- Job Creation in construction, operations, and maintenance, boosting local economies.
Challenges faced by Utility-scale solar projects are:
- Land Use Conflicts with agricultural use, wildlife habitats, and local communities.
- Regulatory and Permit problems are time-consuming and demand compliance with federal, state, and local regulations.
- Interconnection Issues with existing grid infrastructure can lead to technical challenges and might require investment for upgrades.
- Financing for large-scale projects can be complex and difficult, mainly during fluctuating economic conditions.
Community Solar
Community solar refers to multiple participants like homeowners, renters, and businesses together invest and benefit in a solar energy project. Usually, these projects are located off-site and are not directly on the participant’s property. In actuality, the solar panel-generated electricity is sent to the local utility grid. And, participants receive credits on their utility bills depending on their consumption of the produced energy. This approach makes it a useful option, especially for those who do not have suitable rooftops for solar panels.

Community solar projects differ from larger utility-scale solar projects in terms of their accessibility and scale. Generally, utility-scale solar projects are large installations, that generate huge amounts of electricity. And, it usually supplies power directly to the grid and serves a very broad area. The utility companies or large energy developers own and operate these projects and are capable of covering massive areas of land.
In contrast, community solar are smaller-scale projects that are intended to serve local communities. They are more focused on community engagement and participation, by allowing residents to invest in renewable energy without needing to install equipment on their roofs.
Benefits of Community Solar Projects:
- Solar Energy is more accessible to a broader audience.
- Participants can save cost on their electricity bills through credits received.
- Reducing impact on the environment with Zero greenhouse gas emissions.
- Promotes energy independence and does not depend on fossil fuels.
- Improves local economies by providing jobs in the installation, maintenance, and solar management.
Challenges of Community Solar Projects:
- Legal Issues fluctuate from state to state.
- Obtaining funds for community solar projects is very challenging, especially for smaller projects that might not bring in large investors.
- Participation Limitations are not able to cover every interested participant.
- Grid Integration could lead to technical challenges in areas with outdated infrastructure.
Differences Between Residential, Commercial, and Utility Solar Projects
The 3 main types of solar energy projects are residential, commercial, and utility-scale, and each of them has unique characteristics like — efficiency, size, design, installation processes, and environmental impacts.
Here is a detailed comparison of the 3 types of solar projects in a tabular form which would be easier to differentiate:
| COMPARISON | Residential | Commercial | Utility-Scale |
| Efficiency | 15% to 20% (Varies based on Solar Panel Type) | 18% and 22% (Large-scale installations) | Often exceeds 20% (More advanced technology) |
| Size | 3 kW to 10 kW | 100 kW to several megawatts (installed on rooftops or as ground-mounted systems) | Usually exceeds 1 megawatt (supplies power to the grid and serves large populations). |
| Design | Designed to blend with the home’s architecture | larger rooftop installations or ground-mounted arrays | Maximizes land use and energy output with large arrays of solar panels |
| Installation Processes |
|
|
|
| Environmental Impacts | Reduced carbon footprints for individual homes. | Decreases greenhouse gas emissions. | Low-carbon energy system. |
Conclusion
Overall, it is very important to select the right type of solar project to maximize the benefits as well as to stay aligned with one’s particular needs and circumstances. However, you need to consider a few factors while making the decision, which include — financial considerations, energy requirements, and site characteristics.
Ray is an avid reader and writer with over 25 years of experience serving various domestic and multinational private and public energy companies in the USA.