A solar array is a combination of multiple solar panels that work together to convert sunlight into electricity. It is valuable in solar energy systems because many panels simultaneously capture solar energy and transform it into usable electrical power for homes, businesses, and other purposes.
Understanding the composition and functionality of solar arrays is important as it helps you make sensible decisions when it comes to efficiency, cost, and suitability. A thorough knowledge of how solar arrays operate will guide you in making the best use of your solar energy systems for the greatest performance and savings.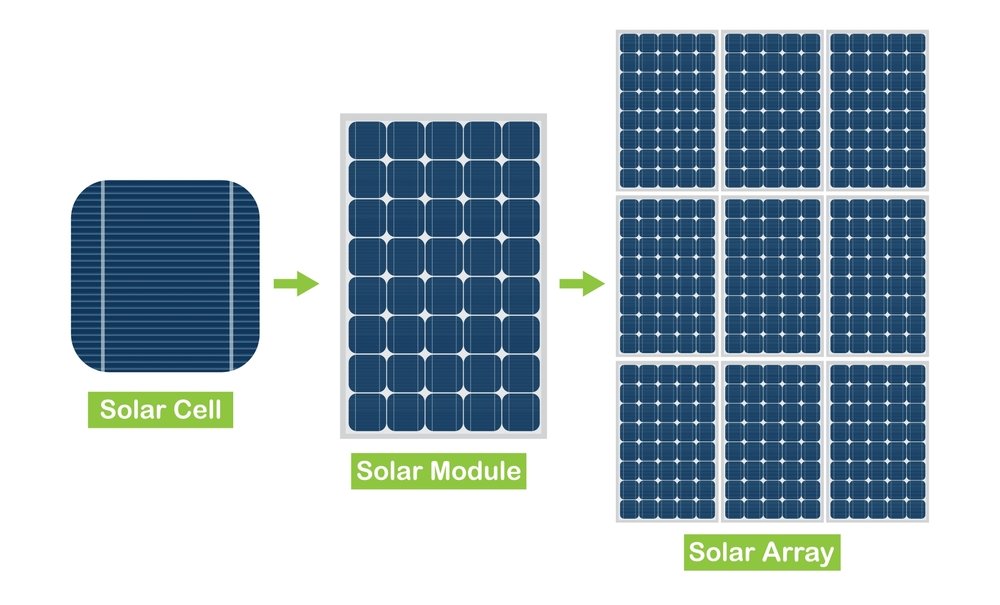
Let us further understand various complications and doubts that arise about installing more than one solar array and whether is it possible to add more solar panels to your solar array.
What are Solar Arrays?
A solar array is a series of more than one solar panel, stacked together, to simultaneously convert sunlight into electricity. Usually, these panels in array are either mounted on rooftops or ground-mounted systems. Designed to capture sunlight efficiently, the major advantage of solar arrays is their ability to generate a very large amount of electricity.
Arrangements of solar panels are done in a special pattern to form an array. However, the sequence of arranging the panels might vary based on the energy needs of the installation. Most commonly, a solar array has panels connected in series and parallel kinds of formation.
- Series connection: Output from the first panel is fed to the next, and it increases the voltage with the process of keeping up the same current.
- Parallel connection: The same voltage source has many panels connected to it, this increases the current while keeping the voltage constant. Flexibility in design can be attained with this arrangement and lets you ensure that the solar array is capable of producing the desired amount of electricity, despite some panels being shaded or not functioning properly.
The construction of solar arrays consists of multiple primary elements that include:
- Solar panels: Developed using photovoltaic (PV) cells, the panels are typically composed of silicon. The most frequently used types of solar panels are monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film panels, and each of them has its unique efficiencies and costs.
- Mounting systems: Usually manufactured using heavy-duty materials like aluminum or galvanized steel, so that it is capable of resisting different weather conditions.
- Electrical components: Includes the inverters and other necessary wiring, which are useful for converting and transferring the electricity generated by the solar panels.
How Does A Solar Array Work?
The working of a solar array happens with a series of panels functioning simultaneously to absorb sunlight and convert it to usable electricity through the “Photovoltaic Effect” process. Rays from the sun hit the solar panels, and silicon in the panels absorbs the sunlight and excites electrons in the semiconductor, allowing them to flow freely.
The different configurations of solar cells within panels are:
- Monocrystalline solar cells: Generally made of a single crystal structure appear sleek black, are highly efficient, and perform well in low-light conditions.
- Polycrystalline solar cells: Made up of multiple crystal structures that appear in a bluish hue are slightly less efficient compared to monocrystalline cells.
- Thin-film solar cells: A thin layer of photovoltaic material is placed on a substrate having a lower efficiency than crystalline cells.
Configurations of solar cells impact the overall performance of the solar array in various aspects such as — efficiency, cost, and space requirements. A higher efficiency cell means more electricity generation.
The arrangement of solar panels in an array affects the system’s efficiency and output based on factors like:
- Proper spacing and minimizing shading from the neighboring panels.
- Choosing between configuration of Series (increases voltage) vs. Parallel (increases current).
- Tracking Systems to adjust the panel orientation according to the sun’s path, increases energy absorption by 25%.
The application of solar arrays varies significantly between residential and large-scale settings:
- Residential Solar Arrays: Being small-sized, these systems are developed to fulfill the energy requirements of a home. Rooftop installations are used to increase space and reduce costs.
- Large-Scale Solar Arrays: These are designed to produce high amounts of electricity and require large areas of land, but reduce the cost per watt of electricity generated.
How Big Are Solar Arrays?
The size of solar arrays can be determined by several factors, including user energy needs, available installation space, and solar panel efficiency. Residential solar arrays commonly range from 5 kW to 10 kW, requiring about 15 to 30 panels (depending upon the panel’s wattage capacity). Whereas, large-scale solar arrays range from hundreds of kW to many MW (a Megawatt equals 1,000 kilowatts).
Location and sunlight intensity have a greater impact on the solar array size because of these factors. States like California and Arizona have higher sunlight intensity, so it might require fewer panels compared to regions with less sunlight, such as the Pacific Northwest. Solar arrays installed in regions with higher sun exposure function more efficiently.
Solar arrays can be customized to fit non-traditional spaces or irregular roof designs, as most solar companies offer many flexible and modular solar panels specially designed to fit various roof shapes and sizes. And, with this customization you can ensure maximizing your solar energy potential, irrespective of your home’s architectural design limitations. In addition, solar technology’s advancement with thin-film solar panels provides you greater installation flexibility.
How Many Solar Panels Are in an Array?
The number of solar panels in an array can be different between residential, commercial, and utility-scale installations as each type has different physical dimensions or requirements like energy needs, available space, and panel sizes.
Here is a detailed comparison for you to clearly differentiate the number of solar panels required on residential, commercial, and utility-scale installations.
| Solar Array Type | Number of Panels | Size of Panels | Power Output |
| Residential | 15 to 24 | 65 inches x 39 inches (1.65 meters x 0.99 meters) | 240W to 420W |
| Commercial | 50 to 100 (or more) | 77 inches x 39 inches (1.96 meters x 0.99 meters) | 330W to 510W |
| Utility Scale | 100 to 1000 (or more) | Similar to Commercial ((but used in much larger configurations) | 330W to 600W |
Several factors influencing number of solar panels required for a solar array are:
- Electricity Consumption: This is the primary factor, as the amount of electricity consumed by the household, business, or utility will help decide the number of solar panels required in an array.
- Location and Sunlight Exposure: Based on the amount of sunlight received in a location, the number of panels is determined. It further influences the energy production results because regions with more sunlight require fewer panels.
- Panel Efficiency: If your panels have higher efficiency ratings, they will provide more electricity per square foot, and this will reduce the number of panels required in an array.
- Roof Space: The available installation space impacts the number of panels required. To increase the energy generation on a roof with less space, you might require installing higher efficiency panels.
- Local Regulations: The design and size of solar installations can be impacted by local rules and incentives, which also influence the number of panels to be used.
Where can Solar Arrays be installed?
These are the most commonly preferred locations for installing solar arrays:
1. Rooftops: Most residential solar arrays prefer rooftops because they utilize unused space, reducing land use. It is used because they have less or no shading issues and can be oriented towards the sun. In the United States, south-facing roofs are preferred for maximum exposure to sunlight.
2. Ground-mounted systems: Residential or Commercial installations with ample land space prefer ground-mounted systems. It is used to position it towards sunlight and is easier than a rooftop in terms of maintenance or cleaning.
3. Solar Farms or Agriculture Lands: Known as “Agrivoltaics”, these systems are used as they can generate higher amounts of electricity without any limitations of urban environments.
Orientations and positions of solar arrays impact their efficiency and power output as the panels have to be tilted matching the latitude of the installation site. As a result, it will optimize the exposure to sunlight, and panels are titled perpendicularly will improve the efficiency.
The installation locations for solar arrays differ between residential, commercial, and utility-scale settings in terms of energy requirements. According to a study in the United States, south-facing solar arrays generate higher power compared to west-facing or east-facing arrays that produce 15% less energy.
While deciding on solar array placement to ensure optimal energy production and system efficiency, property owners must consider a few factors such as:
- Shade
- Roof condition
- Tilt and Orientation
- Local Regulations
Also, offering a few benefits, here are a few innovative or niche locations for solar array installations such as:
- Floating Solar Arrays: Installed on water bodies to reduce evaporation and land use.
- BIPV (Building-Integrated Photovoltaics): Integrated into building materials like windows or doors, offering stylistic and functional benefits.
- Solar Roadways: Roads are coated with solar panels to generate electricity.
What is the Cost of a Solar Array?
The cost of a home solar panel system typically includes several key components such as solar panels, inverters, installation, permitting, and inspection fees.
In the United States, the average cost of a standard home solar panel system is around $30,000 without including any incentives. However, the total cost could drop to $21,000, if federal tax credits and other solar incentives are applied. Solar inverters cost between $1,000 and $3,000, whereas Installation costs range from $1,000 to $3,000.
Several factors that influence the overall cost of a solar panel system are:
- System Size
- Type of Solar Panels
- Location
- Energy Needs
- Roof Characteristics
Additionally, the overall cost of installing a solar panel system can be reduced using a few incentive schemes such as:
- Federal Solar Investment Tax Credit (ITC): You can deduct 30% of solar system installation cost from your federal taxes.
- State and Local Incentives: There are many states and local governments that are currently offering additional tax credits, rebates, and other incentives to promote solar adoption.
- Net Metering: Utility companies are offering net metering programs, allowing you to sell excess electricity back to the grid, compensating or covering your energy costs.
Can You Install More Than One Solar Array?
Yes, you can install more than one solar array, but there are a few circumstances where you would need more than one solar array.
- Increased Energy Consumption: Adding more appliances, Homes, or businesses demands using high amount of electricity and this requires using multiple solar arrays to meet the energy needs.
- Limited Roof Space or Expansion: You might have less space on the roof, or you are willing to renovate, add a building, or expand the space. In any of these cases, you would require multiple solar arrays.
- Maximizing Energy Production: Multiple solar arrays can be placed at different angles and oriented in such a way that they capture more amount of sunlight.
- Redundancy, Reliability, and Grid Independence: If one array underperforms due to shading, multiple solar arrays provide backup. Also, it helps you be independent of the grid.
Multiple solar arrays can be connected in 3 ways to supply electricity effectively:
- Series Configuration: Panels connected end-to-end, increase voltage and keep the current constant.
- Parallel Configuration: Panels connected side-by-side, keeps voltage constant and increases current.
- Combination of both: To connect both series and parallel to maintain a balance between the current and voltage.
The functioning of multiple solar arrays takes place having its own microinverter to enhance efficiency. Also, it has power optimizers, to use with traditional inverters for improving each panel’s output. These multiple arrays can be connected to the grid, which is beneficial for net metering (excess energy fed back into the grid).
Additionally, there are several potential benefits and drawbacks of having more than one solar array:
Benefits of Multiple Solar Arrays:
- Increased Energy Production
- Redundancy
- Flexibility
- Scalability
- The Best Use of Space
Drawbacks of Multiple Solar Arrays:
- Higher Initial Costs
- Complexity in Maintenance
- Space Requirements
Is It Possible to Include Additional Solar Panels in Your Solar Array?
Yes, you can add more solar panels to your solar array, and it is a great way to enhance energy production. But you must understand the reasons, factors, considerations, and challenges that come with adding more solar panels to your existing solar array.
3 Main Reasons in Brief why you should try Expanding Your Solar Panel System:
- Energy consumption increases.
- You are seeking a solution to further reduce your electricity bills.
- Willing to enhance the system’s output.
Factors Impacting Capacity and Efficiency are:
Roof Space
Panel Quality
Local Climate or Shading
Existing system specifications
Tilt and Orientation of Panels
Whenever you are planning to expand a solar array in the future, you must keep in mind a few considerations regarding local and federal incentives, such as:
- Thoroughly check for local and federal incentives that are applicable. For example, the federal solar tax credit offers a 30% tax credit on solar panel installation costs.
- Strictly follow local regulations which might affect your ability to add more panels.
You must ensure using the same installation company for both the original and add-on solar projects because of the warranty continuity. The original installer can stick to existing warranties and make a hassle-free coverage process as they are familiar with your existing setup.
Challenges and Mitigations while adding a few more panels to an existing solar array are:
| Challenges | Mitigations |
| New panels might not be compatible with existing solar arrays. | Check the compatibility and consult a professional before adding panels to the array. |
| Some installers might deny working on solar systems that they didn’t install. | It is recommended to go with the original installer company. |
| It can be costlier to include additional panels to a solar array. | Many incentives and financing options can help to cover the costs. |
Should You Install a Solar Array?
Installing a solar array can be beneficial, but it also comes with a few challenges that you must bear in mind before deciding on installation.
Benefits of Installing a Solar Array:
- Reduces the cost of electricity bills and saves a lot of money over time that covers the initial cost.
- Increases the value of the home that has solar panels installed.
- Minimizes the harmful emissions of GHG (Greenhouse gas) and other pollutants.
- Being a reliable source of energy, installing a solar array further reduces dependency on the grid.
- Various Federal, State, and Local Incentives are available to compensate for the installation cost.
Challenges of Installing a Solar Array:
- Upfront costs or the initial investment are very expensive.
- Not all roofs are suitable for solar panels because of the roof’s age, difficulty in orientation, and shading issues.
- Minimum maintenance is compulsory for the satisfactory performance of the solar panels.
- Storage and Backup solutions are necessary for functioning after sunset also because solar power is dependent on sunlight.
- Regulatory Issues regarding being compliant with local building codes, zoning regulations, and other permitting requirements, can be very challenging.
Considerations you must keep in mind before deciding to install solar arrays are:
- Ensure to check your roof’s age, structure, and orientation.
- Understand your energy consumption to calculate the size of the system required.
- Look to reduce overall costs by checking the federal, state, and local incentives that are applicable.
- Select the best licensed contractor who has good experience to guarantee a quality installation.
- Consider long-term plans and evaluate how long you are going to stay in your home because solar panels can increase your property’s value.
Ray is an avid reader and writer with over 25 years of experience serving various domestic and multinational private and public energy companies in the USA.

