Solar energy is the thermal radiation emitted by the sun harnessed using different technologies to generate electricity that consists of three main types of systems namely Grid-tied, Off-grid, and Hybrid methods having their advantages and disadvantages.
Solar energy has become the most important part of today’s energy landscape due to its positive effects on the environment, reduced reliance on non-renewable sources such as fossil fuels, savings on electricity bills, and job creation in various sectors.
There are mainly three types of solar power systems: grid-tied, off-grid, and hybrid solar systems. Understanding the differences between grid-tied, off-grid, and hybrid systems is essential to finding out the equipment used in each type and deciding which solar power system is right for you.
Grid-Tied Solar Power System
A grid-tied solar system, also known as an on-grid, is permanently connected to the traditional electricity grid and provides energy to your home when sunlight is present. The working process is based on the direct connection to the grid and cannot operate in its absence. The DC electricity is stored in batteries and sent to the inverter to convert it into AC power before being fed directly into the grid.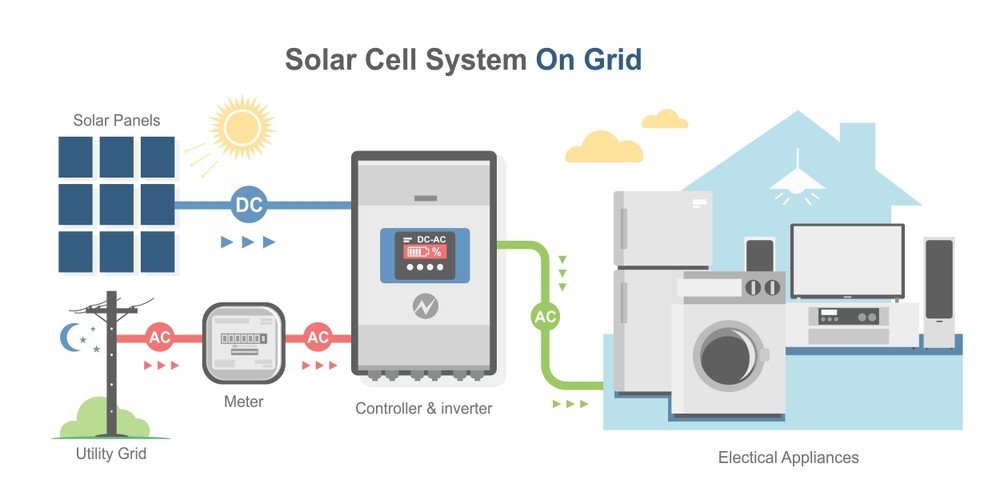
- The initial costs are reduced since you don’t require a battery for energy storage.
- You can use energy to send excess power back to the grid and earn credits from the utility company that helps to lower your electricity bills.
- Requires less maintenance with fewer components and no batteries involved.
Net metering is a billing scheme that uses an electrical grid to store additional energy generated through residential or commercial solar panels. This concept mainly contributes to the cost-effectiveness of grid-tied solar systems. When an excess amount of solar energy is produced, the bidirectional meter operates in the reverse direction to calculate the transfer of electricity units to the grid. You can earn credits from your utility company that can help offset the cost of your current bills. Here is more detailed information about grid-tied solar system.
Advantages of Grid-Tied Solar System
These are the main benefits of using a grid-tied solar system:
- Reduced Installation and Equipment Costs: Grid-tied systems don’t require additional expense of purchasing equipment such as purchasing and maintaining batteries to store energy that can be used for power outages or off-grid purposes.
- Cost Savings and Return on Investment: The power obtained from the grid will be at a reduced price due to the credits received for feeding additional energy to the grid, thereby obtaining a substantial return on investment over a certain time. Additionally, the payback period for the funds invested in your on-grid solar system gradually decreases.
- Utility Grid as Backup Battery: The on-gird solar systems are connected to the utility grid that acts as a backup power source such as a battery that provides accessibility to electricity from the grid during cloudy or nights.
- Flexibility and Scalability: The on-grid systems are easily scalable and have higher flexibility to meet the increased energy needs. It is possible to add extra panels to the existing setup without any huge alterations.
Disadvantages of Grid-Tied Solar System
The main drawback of using a grid-tied solar system is the vulnerability to power outages. As there is too much dependence on the grid, its failure results in the entire system discontinuing its functioning. Particularly, in areas with outdated or limited electrical systems, the net-metering scheme might be unsuitable.
Equipment used for Grid-Tied Solar System
The components used for grid-tied solar systems include:
- Solar Panels are semiconductor materials made of silicon that are wired together to absorb sunlight and generate electricity.
- Racks and Mounts help to grip your solar panel system in one place with properly structured stands that are specifically built to resist harsh weather conditions.
- Combiner Box is a common meeting point where the combined DC outputs of several solar panels are fed into the inverter.
- AC and DC Cables ensure the constant flow of current between the components thereby guaranteeing smooth functioning of the system.
- Grid is the important part of the solar system that acts as a backup or storage system like a battery to transfer additional power and then withdraw when required.
- Grid Tie Inverters convert DC power produced by solar panels into AC power that can either be used to run your home appliances or feed the extra electricity back to the grid.
- Net Meter measures the used energy as well as the additional power sent back to the grid. This bidirectional meter withdraws the left-over units from the grid at night to keep the appliances functioning.
Off-Grid Solar Power System
An off-grid solar system, also known as the standalone power system (SAPS), generates electricity without any dependence on a grid connection and accumulates the energy generated during daylight hours using a battery backup.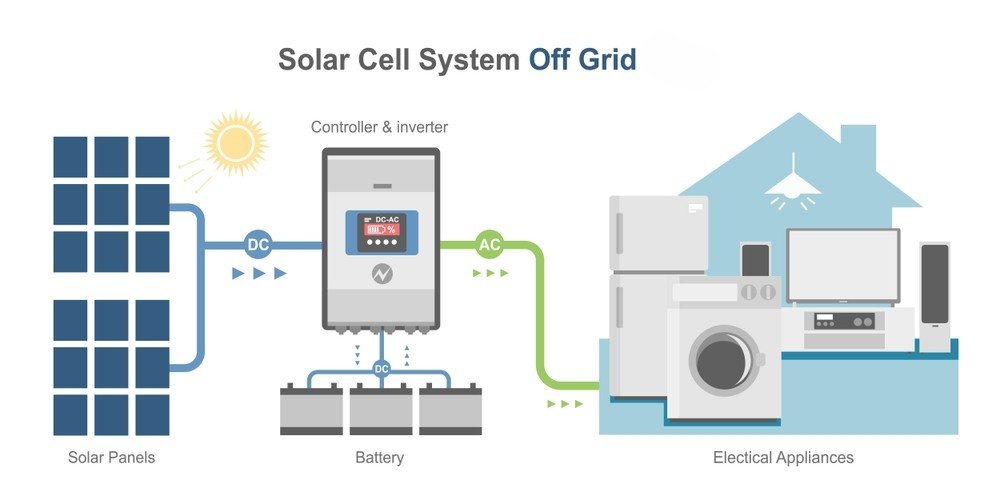
Solar panels generate direct current (DC) and transfer it to the solar charge controller for regulating the flow of electricity as well as prevent overcharging and damage to the battery. Furthermore, the conversion of DC to AC power through an inverter (most often standalone inverters are recommended for off-grid systems) can be used to run electrical devices or accumulate in a solar battery system.
Batteries play a crucial role in off-grid solar systems and energy management ensuring that home appliances run during nights or power outages. As solar panels generate additional electricity during the day, a battery stores the surplus energy rather than wasting it which can be beneficial for future use.
Advantages of Off-Grid Solar System
You need to consider these advantages while using the off-grid solar system:
- Complete Energy Independence: Users aren’t dependent on the electrical grid which means that they can produce electricity on their own and gain absolute control over their energy supply.
- Cost-Effectiveness in Remote Locations: Particularly in rural areas, the budget for extending the power grid can be high, and off-grid solar systems are cost-effective alternatives that can harness solar energy and provide long-term savings on electricity bills.
- Resilience to Blackouts: Off-grid solar systems are resilient to blackouts as they don’t depend on the main power grid. During unpredictable power outages, these systems can supply electricity guaranteeing that the required appliances operate without any interruptions.
Disadvantages of Off-Grid Solar System
The negative sides of using the off-grid solar system include:
- Higher Initial Costs: The upfront costs of an off-grid solar system are higher due to the requirements for batteries, charge controllers, inverters and other types of equipment during the initial setup.
- Complexity in Maintenance: Frequent maintenance is required to guarantee the system functions reliably and batteries need to be replaced every few years since they have a limited lifespan.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Using an off-grid solar system requires energy conservation and careful management of electricity usage by operating fewer appliances. Typically, these systems are designed to fulfill the demands of individual households or small-scale communities.
- Limited Capacity for High Consumption: The energy storage capacity is limited for off-grid solar systems and isn’t suitable to meet the huge consumption needs of the users. Also, it can be challenging to expand the system to provide electricity for large-scale businesses or industries.
Equipment used for Off-Grid Solar System
These are the main equipment used for an off-grid solar system:
1. Solar Panels are the main source of energy for the system that uses the photovoltaic effect to convert sunlight into electricity.
2. Charge Controllers facilitate the energy flow through solar panels and batteries. The two types of charge controllers include:
- PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) solar charge controllers depend on the modulation of the pulse to alter the energy rate transferred from panels to batteries.
- MPPT (Maximum PowerPoint Tracking) solar charge controller is a DC-to-DC converter that regulates the charge of your battery bank.
3. Deep-cycle batteries accumulate the energy generated by solar arrays during the day and can be used during nights or power outages.
4. Solar Inverters operate on the stored DC energy in the battery bank and run your appliances by converting 120V or 240V AC electricity.
Hybrid Solar System
Hybrid solar system also known as the solar plus storage system, the hybrid solar system is a combination of both grid-tied and off-grid solar power systems. In other words, the system is integrated with grid-tied setups through net metering and has a battery backup to store power.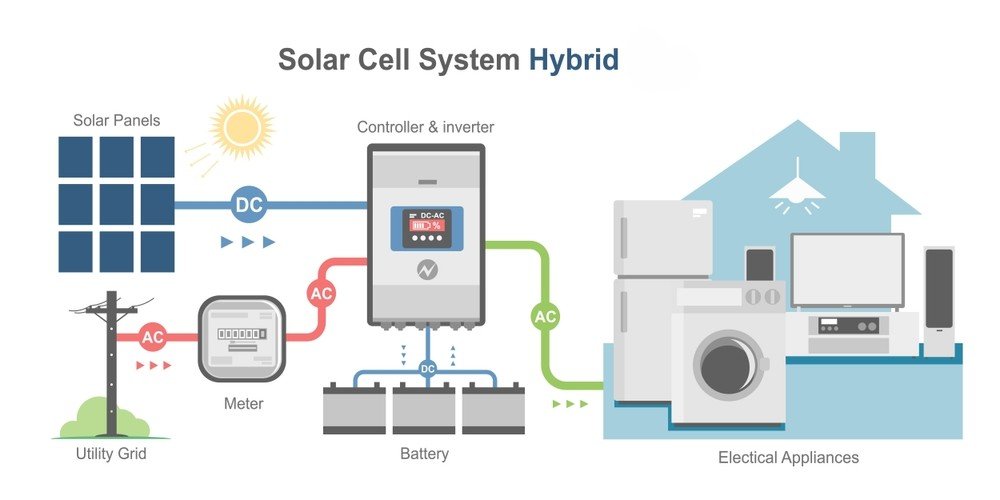
Advantages of Hybrid Solar System
The following are the pros of using the hybrid solar system:
- Cost Efficiency Compared to Off-Grid Systems: Hybrid solar systems are cost-efficient in comparison to off-grid systems because the battery acts as a backup source to store DC power. Also, the grid can be utilized as a virtual battery to minimize the requirement and cost of external batteries.
- Energy Storage and Independence: During periods of low sunlight or power outages, the hybrid system incorporates battery storage thereby increasing the energy independence on the grid.
- Backup Power During Outages: The backup provided during power outages is one of the main advantages of hybrid solar systems that ensures the appliances are running, and the system remains operational even when the grid is down.
Disadvantages of Hybrid Solar System
Here are the cons of using the hybrid solar system:
- Initial Cost of Battery Storage: The initial investment for a hybrid solar system is high due to the inclusion of battery storage.
- Complexity of System Management: Compared to a standard grid-tied system, it is a complex process to manage a hybrid system as it requires balancing energy production, storage, and grid usage. It becomes mandatory to have high knowledge while operating the system.
- Potential Underutilization Without Net Metering: You wouldn’t gain complete benefits of storing excess energy and using it in areas without net metering which leads to underutilization of energy.
Equipment used for Hybrid Solar System
The components used in a Hybrid solar system include:
- Solar Panels are structured either on rooftops or ground-mounted to gain exposure to maximum sunlight that helps in converting solar energy into DC power.
- Hybrid Inverters combine the functionality of microinverters and battery chargers in a single unit. It utilizes the DC power from solar panels and converts it into AC power that can be used for your home appliances. At the same time, the AC power from the grid is used to store DC energy in your batteries.
- Batteries store additional solar energy generated that can be used during power outages, low sunlight, or cloudy days. Additionally, the battery management system helps monitor the charging and discharging of batteries to optimize their usage and lifespan.
- Charge Controllers increase the battery’s lifespan by maximizing the quantity of power entered inside a battery.
- Grid Connection acts as a backup power source to withdraw power from the grid and export additional energy back to the grid, particularly when solar and battery energy is not sufficient.
- Switchboards the residential buildings to use solar energy, send it to the batteries or sell excess electricity to the grid. Wirings connect all the components in your system ensuring the smooth flow of solar power.
- Monitoring systems equipped with energy management features help optimize energy usage and increase its efficiency of flow by maintaining the system’s performance.
Which Solar Power System is Right for Your Needs? Final Opinion
When choosing between grid-tied, hybrid, and off-grid solar systems, these are the important factors you need to consider:
1. Geographical Location (Urban vs Rural): Your property location plays an important role in deciding the type of solar power system. Urban areas have a strong grid infrastructure, but they have limited space with shading issues that reduce efficiency and make it challenging to install solar panel arrays. Rural areas have huge land space and allow larger solar installations, but have less reliable grid infrastructures.
2. Benefits of each type of solar system for different living environments: Each type of solar system has its own advantages of installing for different living environments. For instance, a grid-tied system is less expensive when compared to off-grid systems and is suitable for urban areas where excess energy can be transferred back to the grid. But, they wouldn’t be suitable to fulfill every individual’s demands. On the other side, off-grid or hybrid systems can be installed in rural areas where a battery backup source plays a major role.
3. Availability of roof space and local grid infrastructure: Check your roof is structurally stable and has sufficient space for installation. Also, the choice of solar system is influenced by the quality and reliability of the local grid, particularly in areas with frequent outages, where hybrid or off-grid systems are highly suitable.
4. Role of Local Experts: Local experts can assist homeowners and businesses in making the right decision by helping them evaluate energy consumption, optimize system design, and help comply with local regulations.
Ray is an avid reader and writer with over 25 years of experience serving various domestic and multinational private and public energy companies in the USA.

