Solar Inverters, also known as photovoltaic inverters, are the essential components of the PV system, which can be used to power your electrical appliances in homes and businesses. They are available in several categories such as power optimizers, string inverters, microinverters, and hybrid inverters.
Just imagine, what if the solar panels produce energy without inverters? Certainly, the power generated would be incompatible with several electrical devices and systems.

Modern solar inverters ensure the best functionality of the solar system at maximum efficiency by optimizing the power output from solar panels. You need to choose the right inverter for effective solar energy utilization.
This guide will assist you in exploring the different types and sizes of solar inverters and how to select the best module by analyzing its cost, lifespan, and popularity in the market. Most importantly, you should understand the concept of AC vs DC electricity in detail.
What Are Solar Inverters?
Solar inverters serve the fundamental function of performing the conversion process of direct current (DC) output from solar panels into alternating current (AC).
Beyond the DC-to-AC conversion process, solar inverters play a significant role in maximizing the power output, providing two-way communication to support the grid operations and minimising risk by shutting down if in case any electrical fault occurs. A few solar inverters provide real-time monitoring data about system performance that helps to rectify the issues rapidly and guarantees the best possible energy production.
Grid-tie inverters are the electrical components connected to PV panels, used to harness solar energy and convert DC into AC with a power grid frequency ranging from 50Hz-60 Hz to operate local electrical generators. Typically, the energy is fed into the electrical system of the household and then to the utility grid. These inverters don’t require any batteries to work and can be used for solar panels, wind turbines and hydroelectric power plants.
In contrast, solar charge controllers are mandatory for off-grid and hybrid systems that require a battery for energy storage. Its main function is to direct the electricity flow from the solar panels to batteries, thereby preventing excessive charging and ensuring effective battery performance.
What is AC vs DC Electricity?
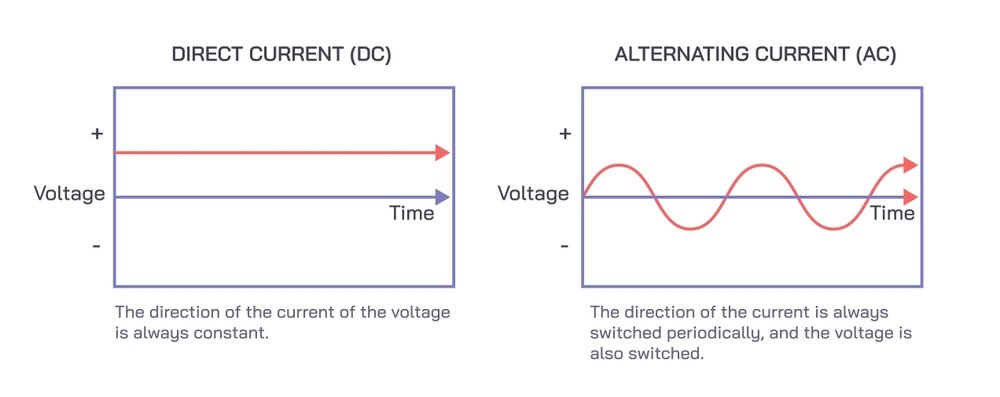
| S.No | Factors | Alternating Current | Direct Current |
| 1. | Electron Flow Direction | Back and forth direction periodically | Single Direction |
| 2. | Wave Form | Sine Wave | No waveform due to constant voltage |
| 3. | Cause | Rotating magnets cause changes in the electrical flow direction. | Steady magnetism |
| 4. | Frequency | 50 Hz to 60 Hz | Zero frequency |
| 5. | Units | Hertz (Hz) | NA |
| 6. | Applications | Electrically powered motors, that are used in refrigerators, washing machines and several other electrical appliances. | Used in smartphone batteries, torchlights, Flat TVs and Electric Vehicles (EVs) |
DC to AC conversion process is essential for solar power utilization in homes. This is because DC electricity cannot be used directly to ensure the appliances’ safety and AC power can be effortlessly converted into high voltages using transformers. It helps to diminish the transmission losses. Also, the conversion process wouldn’t be 100% efficient, since there will be at least 2% or more loss in the electrical energy of a PV solar system, depending upon the quality of the inverter used.
What are the different types of Solar Inverters?
The comparison of four main types of solar inverters classified based on their suitability for various solar power system designs, uses, advantages, & disadvantages:
1. String Inverters:
Mainly, string inverters are installed on your home, closer to your electric meter or service panel.
System Design and Uses:
A string of solar panels mounted on the rooftop of your house in large groups performs the conversion of electrical currents from all solar panels in one location.
PROS:
- Simple in design and easy to troubleshoot.
- Easier and more cost-effective option to add extra panels.
CONS:
- Expensive than string inverters and power optimizers.
- Lower efficiency due to shade or single panel.
2. Microinverters:

Although microinverters carry out similar functionality to string inverters, they are strategically placed at the bottom of each solar panel mounted on your roof.
System Design and Uses:
A preferred choice for residential solar users with parallel circuit connection.
PROS:
- Panels operate independently and wouldn’t reduce output due to excess shade.
- Easier and Cost-effective option to add extra panels.
- Minimum warranty of 25 years.
CONS:
- More failure points.
- Complexity in maintenance and repair.
3. Power Optimizers:

Each solar panel’s power is maximized in a string inverter system by attaching to power optimizers.
System Design and Uses:
These optimizers are attached to the rear end of the panel to track the maximum power output.
PROS:
- Improved shading performance by regulating voltage before power gets sent to the string inverter.
- Panel level monitoring.
CONS:
- Requires additional parts and wiring.
- Additional cost for string inverter and optimizers.
4. Hybrid Inverters:
The pairing of solar systems with battery storage uses a hybrid inverter.
System Design and Uses:
Connecting the panels, battery, grid, and home appliances in one unit in a streamlined design.
PROS:
- Highly efficient.
CONS:
- Less familiar since more batteries are sold along with in-built inverters.
You can also learn more about the types of solar inverters.
How Much Does a Solar Inverter Cost?
The price range for each type of inverter varies depending on several reasons highlighted in the below examples:
1. String Inverters:
String Inverters are less expensive since they require fewer hours for installation. It is a cost-effective inverter and the units are cheaper if your roof isn’t shaded and the panels are facing in the same direction.
- Cost per watt: $0.75
- 1 kW system price: $1,000
- 10 kW system price: $7,500
2. Microinverters:
Due to their long-term performance, microinverters are worth the expensive investment to support the complex design of your roof.
- Cost per watt: $1.15
- Overall Cost: $1,150 to $11,500 (for 1kW to 10 kW system)
3. Power Optimizers:
Compared to microinverters, power optimizers are slightly less expensive. Since these optimizers will be installed on each solar panel, the overall cost proves to be much higher than standard string inverters.
- Cost per watt: $1.00
- Overall Cost: $1,000 to $10,000 (for 1kW to 10 kW system)
4. Hybrid Inverters:
The Hybrid inverters are expensive due to their dual functionality of a battery backup system and save your expenses in the long run.
- Cost per watt: $0.15 to $0.25
- Overall Cost: $1,000 to $3,000 or more.
Additionally, these are the factors that affect the price of a solar inverter:
- Power Ratings are often measured in Kilowatts (kW). Higher power rating panels are linked with costly prices.
- Brand and Service: Established brands hold a good reputation for their best reliability and superior quality.
- Installation and extra components: The installation cost and additional equipment such as monitoring systems or battery storage vary for each type of inverter, thereby adding to the overall cost.
String inverters are the budget-friendly choice whereas micro and hybrid inverters are highly expensive due to advanced features. Additionally, you can read in detail to know the cost of different solar inverters.
What Size of Solar Inverter Do I Need?
Based on the number of panels of your solar system or array, the size of your solar inverter varies, which can be determined by calculating the wattage of your solar array and finding a compatible inverter satisfying the measurement. Ensure that while selecting an inverter it is greater or equal to the power output of your solar array.
Properly sizing the solar inverters is extremely important to determine the maximum power a solar panel can produce and the household energy consumption. For instance, if a solar panel has a maximum output of 1000 watts, then you require an inverter with at least 1000 watts.
In such cases, smaller capacity inverters wouldn’t be able to handle the complete output of your solar panels, and you wouldn’t be able to extract the most of your investment. Conversely, if you select an inverter that is too large, you would be wasting extra money on a device that is more than your requirements.
Solar inverter clipping occurs when the DC power output from the solar array exceeds the acceptable input level for the inverter. In other words, As a result, the inverter alters the DC voltage to reduce the DC power, which can be achieved by increasing the voltage above the MPP voltage.
Inverter clipping frequently occurs in PV systems with DC-to-AC ratios higher than 1.4: 1. Certain factors like your location, solar panel array size and its DC power output related to the inverter’s AC output influence the clipping factors.
There are certain ways you could follow to avoid clipping such as:
- Altering the solar array size.
- Frequent monitoring and maintenance.
- Advanced inverter features which include maximum power point tracking (MPPT) algorithms.
- Installing battery storage systems.
- Proper system design for maximum energy production.
How Long Does a Solar Inverter Last?
Typically, solar inverters on panels last between 10 and 25 years, depending on the brand and the different types you use. For instance, power optimizers string and hybrid inverters have an average lifespan of 10 to 15 years, whereas microinverters have a longer service life of 20 to 25 years.
Several factors affect the life cycle of solar inverters such as:
- Manufacturing quality
- Indoor temperature
- Input voltage and current
- External environment conditions
- Maintenance and cleaning
- Faulty codes
Besides this, there is much more to know about solar inverter warranties. You should know all the important things about solar inverter warranties. It will help you to decide which type of solar inverter will be right for your solar panel system.
However, there are effective ways by which you can extend the lifespan of solar inverters such as:
- Avoid overloading your solar inverter: Overloading causes excess heating and possible damage to the solar inverter, reducing its lifespan. Integrating the inverter with the battery minimizes the load and handles huge electricity demand during regular power outages.
- Check for voltage fluctuations: Voltage fluctuations can minimize the lifespan and efficiency and adding a battery acts as a buffer to absorb extra voltage and offer additional protection.
- Evaluate Malfunctioning: It is important to check the battery’s performance regularly and change it immediately if you observe any malfunctioning.
- Professional installation: Considering the safety and handling issues, the solar inverters must be set up by a professional installer.
- Check for best warranties: Typically, residential solar inverter comes with a warranty period of 5 to 10 years with few having the option to extend upto 20 years (based on the type and brand you use) covering the material, labor, shipping and handling costs. In particular, warranties from reputed brands play a crucial role in financial protection, long-term reliability, system performance assurance, transferability to new homeowners and increased property value (if you sell your property).
How Should You Select the Right Solar Inverter?
As a potential buyer, it is important to ask these questions yourself before purchasing the right solar inverter by considering important factors such as:
- What are my long-term energy storage and backup power needs?
Based on your long-term plans select the battery with the best storage capacity and higher depth of discharge (DoD) for longer backups, integrating with the functionality of inverters.
- How do my roof’s layout and potential shading impact my choice of inverter?
Evaluating the available roof space for solar panel installation helps you choose the best inverters that are compact to easily fit into tight spaces as well as mitigate the shading effects. For instance, microinverters operate independently and provide effective output despite having excess shade, whereas string inverters are highly sensitive to shading.
- What is the total power output requirement of my household or business?
You need to select an inverter with a power output that is the same as your solar panels installed in your residential or business areas. It refers to the maximum amount of AC electricity an inverter can produce. Since solar inverters feature different power ratings, their surge rating varies from device to device or between the same brands.
- How important are the warranty and maintenance implications of the inverter type I choose?
You should choose the best warranty that can protect your investment and maintenance costs if your inverter has any defects or malfunctions. When selecting a solar inverter, you should keep in mind the warranty length, service provided, manufacturer’s reputation and outstanding customer support.
What Are Some Popular and Best Solar Inverters in the Market?
As of 2024, here are a few popular and best solar inverters in the market that offer the best warranty period tabulated below:
| S.No | Brand | Model | Warranty Period |
| 1. | Fronius | GEN24 | 10 Years |
| 2. | SolarEdge | GENESIS | 12 Years |
| 3. | SMA | Sunny Boy | 10 Years |
| 4. | Huawei | SUN2000 Series | 10 Years |
| 5. | Sungrow | SG-RS Series | 10 Years |
Ray is an avid reader and writer with over 25 years of experience serving various domestic and multinational private and public energy companies in the USA.



