Solar Energy is the radiant light and heat emitted by the sun that is converted into electricity through the photovoltaic process. Over the years, the solar industry has progressed with the latest developments in technology by aiming to increase efficiency from 15% in 2010 to more than 22% to 25% (For silicon solar cells) in 2023. Gradually, it led to the introduction of many variants such as the latest night-time solar plants, perovskite solar cells, sun-tracking solar cells, printable solar cells and several others.
The advancements in BIPV (Building Integrated Photovoltaics) strengthen the relationship between PV technology and architecture, without compromising aesthetics and functionality. Incorporating solar panels into building design and construction not only helps to generate electricity but also reduces carbon footprint as well as ensures proper shading, insulation, illumination, and air circulation.
It’s time to explore interesting facts about the BIPV types, their cost, advantages, and disadvantages as well as the top manufacturers in detail.
What is BIPV?
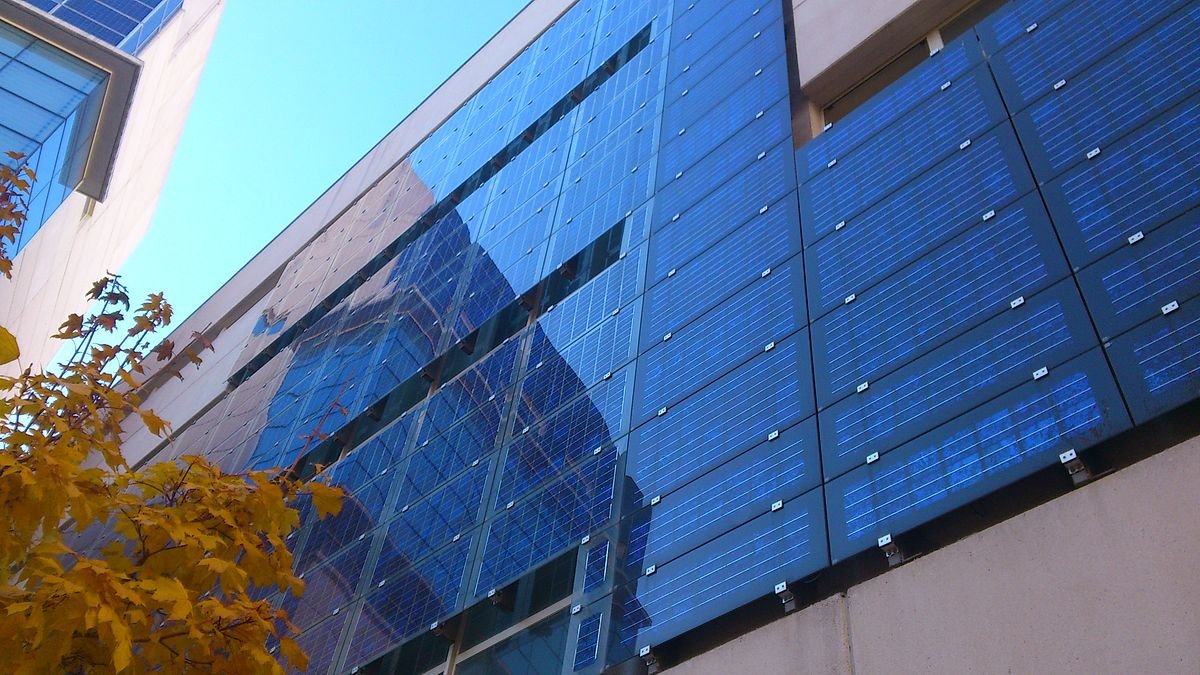

Building Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV) uses PV (Photovoltaic) materials as a source of electrical power to replace conventional building components such as roofs, skylights, exterior walls, doors, and windows.
Despite the pleasing aesthetical appearance of BIPV panels, they still need to be more efficient and have higher upfront costs due to the complex installation process.
BIPV systems are an integral component of the building’s structure that can be installed during the construction of a building or deployed in the modification process of an existing building as replaced components. They can be used in three main application areas, such as:
Roofs: Shingles, Tiles, Skylights.
Facades: Protective cover, Curtain walls and Windows
Exterior-oriented integrated systems: Balcony railings and shading systems
Furthermore, the BIPV along with providing architectural aesthetics serves dual functions — generating electricity along with weather protection abilities such as:
- Waterproofing
- Sun protection
- Thermal insulation
- Resistance to Noise Pollution
- Daylight illumination
- And many safety purposes…
Types of BIPV Systems
Here are the three main types of BIPV systems mentioned below:
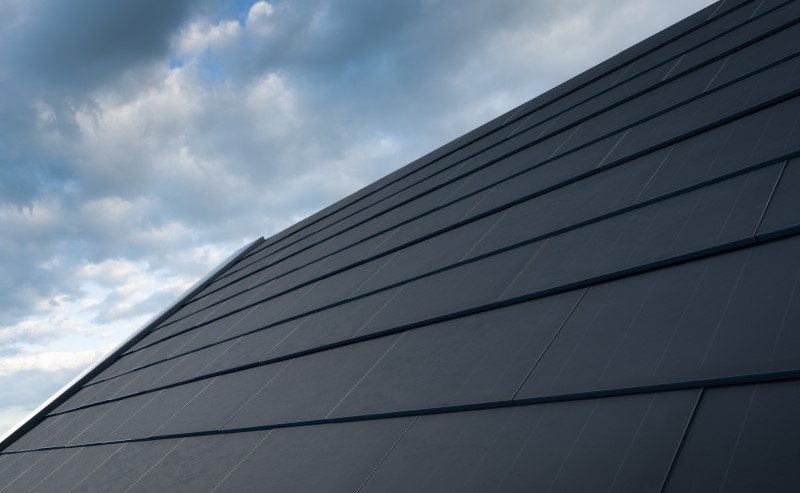
1. PV roof tiles also known as solar shingles add to or replace the existing shingles on a roof to absorb sunlight and convert it into electricity. Similar to the size of the traditional roofing shingles, the solar shingles are 12 inches wide by 86 inches long and weigh approximately 13 pounds/ sq ft. A majority of solar shingles made up of CIGS materials reduce the utility bill by 40 to 70% by increasing the number of tiles to enhance the output. Examples include Monocrystalline Solar Tiles (operates from -40 °C to 90 °C) and Hybrid solar tiles (includes tempered glass, clay, asphalt, and ceramic).

2. Photovoltaic windows are dark-coloured sheets designed using quantum dot technology to absorb more sunlight and convert it into electricity. A thin photovoltaic film made of organic semiconductors is layered on the top surface of the glass. Examples of PV windows are Physee PowerWindow in the Netherlands, with 15,000 installations in office buildings containing power generation abilities and sensor technology to manage building energy consumption.
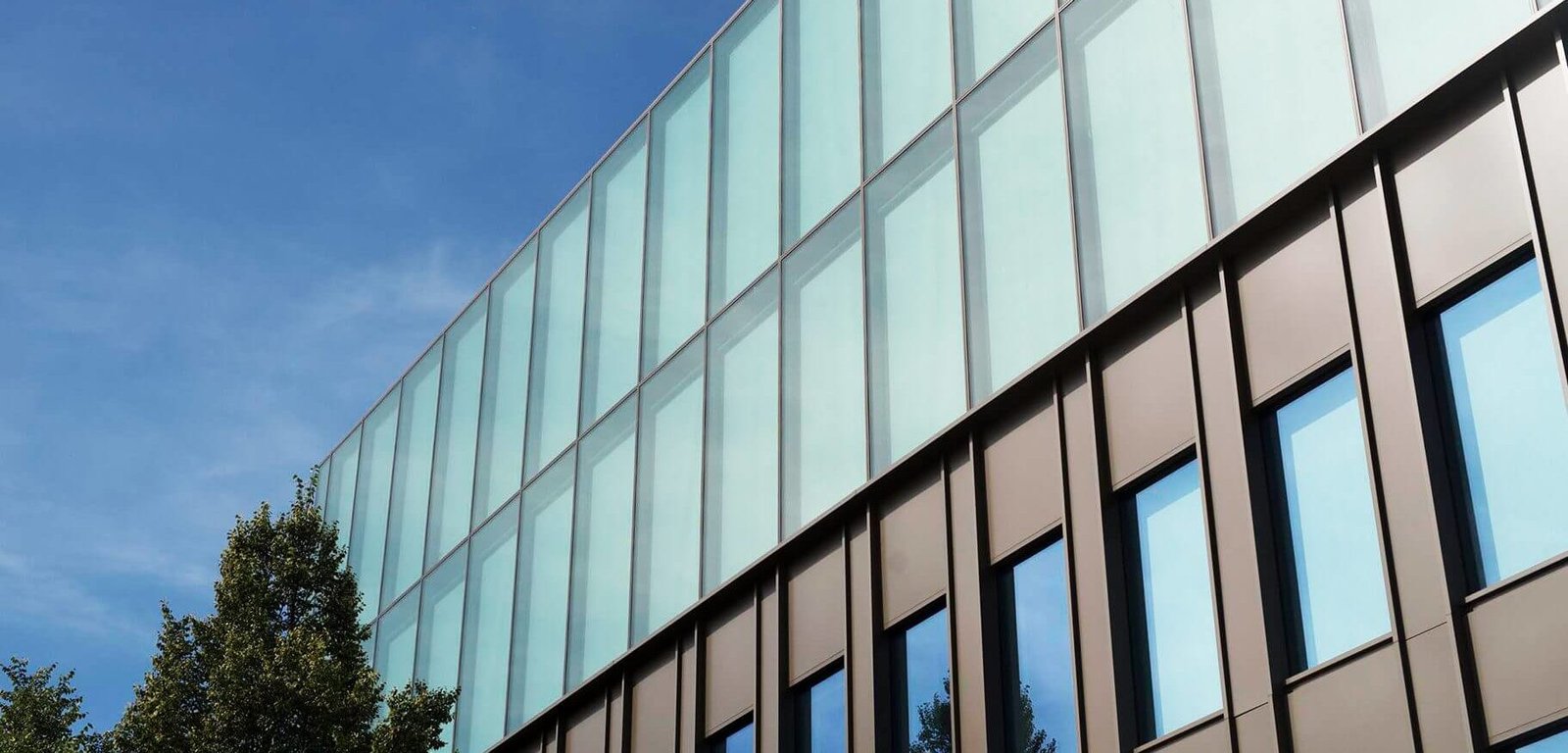

3. Solar Facades are the core components for indoor lighting and radiant environments, and solar energy utilization and control are specifically designed to reutilize, release or absorb heat. Examples of solar facades include Al Bahr Towers in Abu Dhabi, which protects the building from heat and decreases the requirement for air-conditioning.
Other applications include integrating into building structures such as balconies, railings, skylights, canopies, and bricks without compromising visual appeal, thereby offering a promising solution to combine renewable energy into the constructed surroundings for electricity generation.

Advantages of BIPV Systems
Here are some prime benefits of BIPV systems:
1. Multi-function: BIPV serves the dual purpose of producing electricity and maintaining the aesthetics of the building by allowing a perfect combination of solar technology with a building design that leads to visually pleasing structures with stunning roofs or elegant glass facades.
2. Low property power cost: BIPV generates electricity by reducing a building’s dependence on standard energy sources, which can be costly. Consequently, house owners can benefit from lower electricity bills. Additionally, BIPV provides long-term financial gains and prevents fluctuations in energy prices.
3. Enhanced property value: Properties combined with BIPV have a higher value in the market. It is because of the BIPV system signals that maintain higher efficiency and sustainability which makes it appealing for cautious buyers and investors.
Furthermore, these systems increase the market value of a building with its attractiveness. Moreover, the demand for green buildings is increasing at peak level, the property owners can have a profitable advantage in the real estate market, which results in higher resale value and returns on investment(ROI).
Disadvantages of BIPV Systems
Despite possessing some good advantages, the BIPV system faces certain challenges that become its disadvantages, as follows:
1. Requires High Initial Investment: BIPV systems are usually costlier compared to traditional photovoltaic systems. This is mainly because of a few factors like — supply chain issues, extra labour costs, differentiated visual design, technology design, and installation. Despite being expensive, BIPV systems add value to the construction process by replacing traditional construction materials and rack-mounting hardware.
2. Lower Efficiency: The efficiency of BIPV systems tends to vary depending on the design and technology. Most importantly, BIPV efficiency is a bit lower than traditional PV panels efficiency, and this is because the BIPV modules are exposed to much higher temperatures. Because they are directly in contact with the building surface, they don’t allow airflow between the module and the host structure. Also, higher temperatures degrade the semiconducting material of the module, decreasing efficiency very quickly.
3. Longer Payback Period: BIPV systems’ payback periods are often longer compared to traditional PV systems. This is because of the expensive initial investment and lower efficiency. However, the payback period will differ based on certain circumstances, such as — local weather, electricity rates, and government incentives.
4. Specialized Maintenance Required: The installation and maintenance of BIPV systems will need advanced knowledge and skills. Hence, it involves understanding the connection between the building’s structure and electrical system. Also, it requires having the ability to troubleshoot and solve the system as necessary. Therefore, all these aspects add up to the overall cost and system complexity.
How much does Building Integrated Photovoltaics cost?
Building Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV) systems are a significant investment, and their cost can vary based on several factors. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
The Estimate of BIPV Cost Ranges in the US Market according to the global BIPV market size was approximated at USD 19.82 billion in 2022. Although, it is expected to reach USD 42.3 billion by 2026. Thus, further anticipated to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 21.0% from 2023 to 2030.
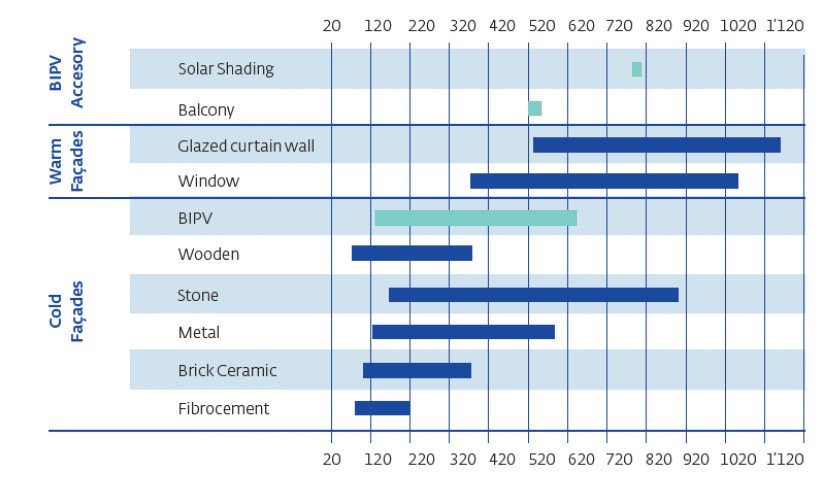
However, the Price in Cost per Unit Area for most of the BIPV systems ranges between $240/m² – $600/m². Also, these costs keep varying depending on the technology used, the installation complexity along with few other factors.
Moreover, the installation cost of a residential PV system in the US is based on the dollar per installed watt (without any government financial incentives). For instance, a PV system and the labour cost for installation might come up to $8 to $10 per watt. However, this cost varies depending on the technical characteristics of the BIPV system and the installation complexity.
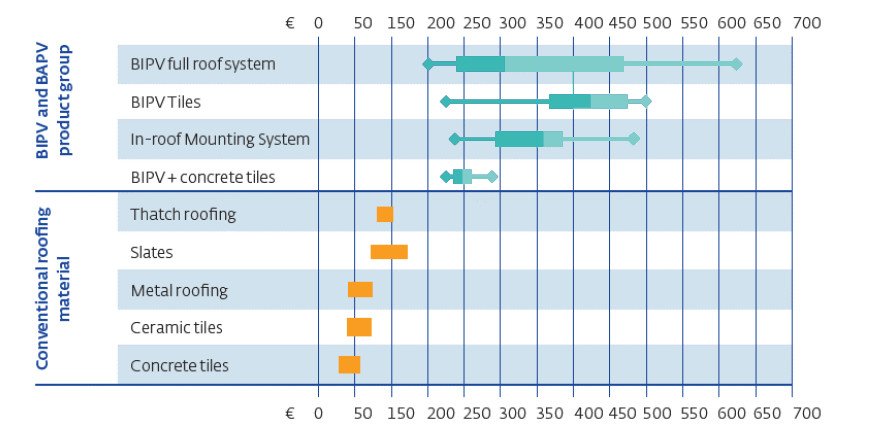
Here are the factors that affect the Cost of Building Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV):
- The technology used for the BIPV modules.
- Installation complexities.
- Needs expertise knowledge and skills.
- Building’s Technical details (where the system is being installed).
- Local weather conditions.
- Electricity costs.
- Government incentives.
What are the Top Manufacturers of BIPV?
Several top manufacturers are widely recognized for their Building Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV). Here are the current top 5 manufacturers that sell BIPV in the USA:
- First Solar
- Sonali Solar USA, LLC
- Solaria Corporation
- P Solar International Inc
- Prism Solar
Ray is an avid reader and writer with over 25 years of experience serving various domestic and multinational private and public energy companies in the USA.

