Solar energy has been experiencing a surge in popularity. Its decreasing costs and developing technologies are making it beneficial, which has attracted many individuals to adapt to solar power as a dependable alternative to traditional energy sources.
There are many compelling reasons why individuals and households are choosing off-grid solar systems over other types. Major reasons for this include grid independence, backup electricity, reduced reliance on utility companies, and rising energy costs. On top of that, off-grid solar systems can be very beneficial in remote locations where the electrical grid is limited or does not exist.
When you go off-grid, the immediate question is what type of battery and solar panel should be used. But should you go off-grid? For that, you must first understand what an off-grid solar system is, what its components are, and its pros and cons.
Also, let us discuss the cost and factors influencing off-grid system cost by comparing it to the on-grid solar system and concerning various aspects. Out of which the main ones include their energy storage, access to electrical power, cost of solar power systems, resilience to power outages, costs of solar installations, installation challenges, and equipment options.
What is an Off-Grid Solar System?
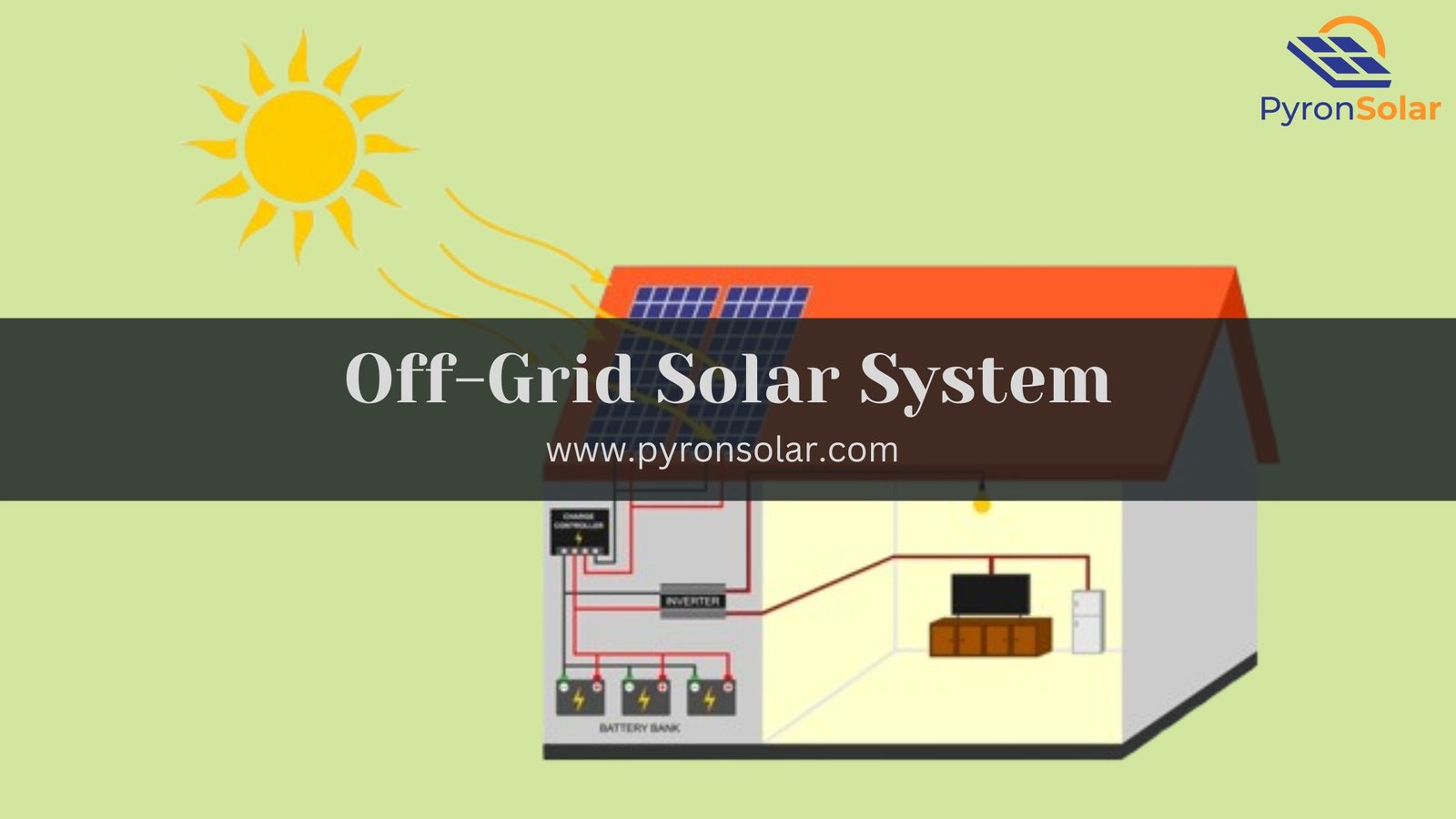
Compared to a traditional grid, the off-grid solar system functions independently and is made to generate, store, and utilize solar energy without depending on external power sources. Generally, an off-grid system involves the use of solar panels, a charge controller, batteries for energy storage, and an inverter to convert the stored DC (direct current) electricity into AC (alternating current) electricity, which is usable for household appliances.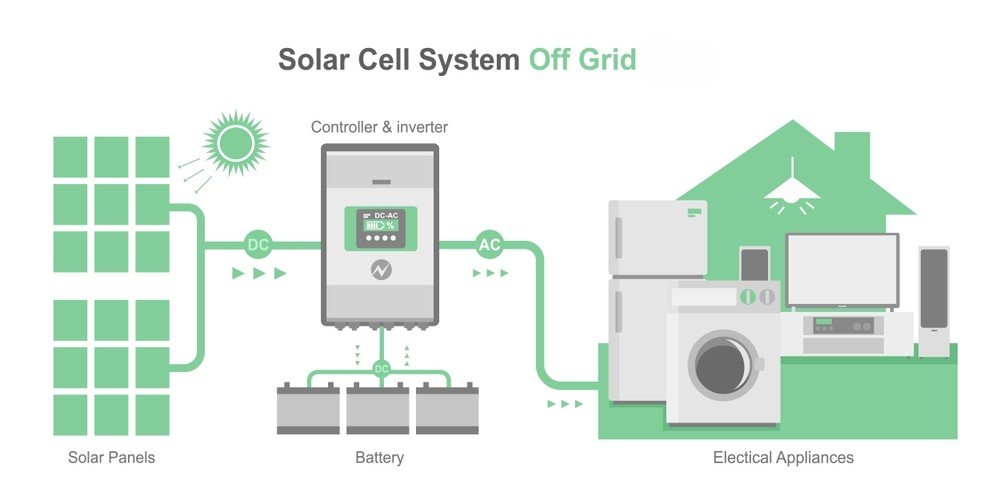
- Rural areas with far distances from utility lines and do not have access to grid connections.
- Camps and other outdoor recreational properties where powering appliances is necessary.
- Disaster-prone regions that unfortunately have prolonged power outages will need off-grid systems as a reliable power source during emergencies.
- Eco-friendly homes that prioritize using renewable energy to minimize their carbon footprint and live sustainably opt for off-grid solar systems rather than traditional methods.
Components of an Off-Grid Solar System
An off-grid solar system is developed to operate independently without using a traditional power grid, providing solar power for homes or factories in remote locations. Below are some key components of the off-grid solar system, along with their functions and importance.
1. Solar Panels
- Function: Solar panels, or photovoltaic panels, made of silicon cells generate DC (direct current) by absorbing sunlight.
- Importance: The efficiency and capacity of solar panels are important as they influence the amount of electricity generated.
2. Charge Controller
- Function: Prevents overcharging and deep discharging by regulating voltage and current passing from the solar panels to the batteries.
- Importance: Extends battery lifespan by ensuring proper charge of batteries to maintain system efficiency.
3. Battery Bank
- Function: Solar batteries stores solar panel-generated electricity for later usage after sunset or cloudy days.
- Importance: Ensures power availability all the time, making it a reliable power supply, especially in remote areas.
4. Inverter
- Function: Solar inverter converts panel-generated and battery-stored DC electricity into AC, which is used in household appliances.
- Importance: Makes stored energy usable for everyday appliances and devices, which supplies power like a standard utility grid.
5. Mounting System
- Function: Keeps solar panels positioned at a highly favorable angle to capture more sunlight and keeps them secured to the roof or ground.
- Importance: Influences durability and efficiency with its sturdy design and protects solar panels from wind and snow.
6. Wiring and electrical components
- Function: Wiring, fuses, and circuit breakers connect the different components of the solar system.
- Importance: Ensures safety, efficiency, and proper electricity flow by right wiring between solar panels, batteries, inverters, and appliances.
7. Monitoring System
- Function: A monitoring system keeps track of the solar system’s performance, including energy generation, battery reliability, and overall system stability.
- Importance: Monitoring systems provide valuable data to help optimize energy usage and identify potential issues before they become significant problems.
Pros and Cons of Off-Grid Solar System
Here are the pros and cons of the off-grid solar system.
Pros of Off-Grid Solar Systems
- Energy Independence: Owning an off-grid solar system means being able to generate your electricity. And, this independence from the utility grid is beneficial because you are less affected by the rising energy costs and power outages.
- Environmental Benefits: A decrease in GHG (Greenhouse Gas) is very advantageous because off-grid solar systems help you tackle climatic changes by keeping your home powered all the time.
- Cost Savings: Despite high initial investment, the off-grid solar system saves electricity bills for the long term. In addition to that, you can benefit from incentives and tax credits to minimize installation costs.
- Increased Property Value: Homes that are installed with solar systems have a great property value and buyers show interest in purchasing it.
- Resilience Against Natural Disasters: Off-grid solar systems act as the best source in emergencies and natural disasters, sustaining hurricanes, wildfires, or other extreme climates.
Cons of Off-Grid Solar Systems
- High Initial Costs: The upfront cost for purchasing and installing an off-grid solar system includes the price of solar panels, batteries, inverters, and installation.
- Maintenance Requirements: Off-grid systems demand more constant and regular maintenance, including proper cleaning of solar panels, monitoring battery health, and replacing components as needed.
- Energy Storage Limitations: Off-grid systems depend a lot on battery storage and provide electricity when sunlight is not available. However, battery capacity limits energy available during cloudy days or at night.
- Space Requirements: Installing an off-grid solar system requires large space for panels and batteries. In urban areas, there is limited space, and it is very challenging to accommodate an off-grid solar system. However, an individual could consider using the nearest land or terrace options to install an off-grid system with its required battery backup.
- Depending on Weather: Typically, weather conditions affect solar panel efficiency. Especially cloudy or rainy weather decreases energy production and further makes it compulsory to have backup power or a well-sized battery system.
How Much Does It Cost to Go Off-Grid?
Typically, setting up an off-grid solar system starts at $10,000 for a 4 kW system to $30,000 for a 16 kW system and more.
Calculating your home’s daily energy usage to determine the size of the solar panel and battery system is possible in the following ways:
- Solar Panel Size = (Daily Load in kWh) / (Location’s Irradiance)
- Battery Size = (Daily Load) x (Number of Days) / (System Volts)
Here is a rough estimation of the costs of solar panels, batteries, and other system components that add up in an off-grid setup in the following ways:
- Solar Panels: $735-$1,176 per panel, producing 250 to 400W power.
- Charge Controller: $50 to $200 per battery bank.
- Inverter: $1,500-$13,000 per inverter for a medium-sized system.
- Battery Bank: $200 to $1,000 per kWh of capacity.
The system sizes and configurations for off-grid solar systems vary according to the approximate estimation, which indicates that these costs are higher compared to being connected to the utility grid:
- Small Systems (1-2 kW): $5,000 to $10,000 (small cabins and RVs)
- Medium Systems (3-5 kW): $15,000 to $25,000 (small homes)
- Large Systems (6 kW and more): $30,000 to $65,000 (Larger homes and businesses).
Additional expenses such as installation labor costs ($3,000 to $8,000) and the potential need for backup generators ($6,000 – $11,000) could add up to the overall cost.
Few financial incentives and rebates such as net metering, federal investment tax credit (ITC), and property tax exemption can help offset the costs of going off-grid.
The long-term savings and benefits of investing in an off-grid solar system compared to on-grid ones help in the following ways:
- Lower electricity bills
- Gain benefits of tax benefits and rebates
- Fewer maintenance costs
- Energy independence
- Resilience against power outages
An Example to Calculate The Total Cost of Going Off-grid
Let’s consider a simple example of a 5kW off-grid solar system to calculate the overall cost:
- Solar Panels: $12,000
- Battery Bank: $8,500
- Charge Controller: $2500
- Inverter: $2,000
- Installation Labor: $2,830
- Backup Generator: $9,000
Adding the above-mentioned expenses, the total cost of going off-grid solar for a 5kW capacity ranges up to $36,830 approximately including the additional charges such as labor and a backup generator.
What factors influence the cost of an off-grid solar system?
These are the factors that influence the cost of an off-grid solar system:
- Location: The off-grid’s geographical location plays an important role in determining the cost as areas with abundant sunlight availability and an average number of peak hours determine the number of solar panels required.
- System Size: Large-sized systems result in higher costs due to increased solar panels, batteries, and other components.
- Mount and wiring: The mounting structure and wire length required are mandatory to connect the components and if the installations are complex, then huge labor expense is required.
- Additional features like backup power sources: Adding backup power sources such as backup generators could increase the cost by $6,000 – $11,000, whereas high-capacity batteries could range upto $10,000 to $30,000 approximately.
- Maintenance: The off-grid solar system requires frequent maintenance such as inspection, cleaning, and changing the components over a certain time, thereby increasing the ongoing maintenance costs.
Comparing On-grid and Off-Grid Solar Systems
Here is a brief comparison between on-grid and off-grid systems:
| S.No | Factors | On-Grid | Off-Grid |
| 1. | Connection | Connected directly to the power grid. | Not connected to any power source. |
| 2. | Upfront Costs | Less Upfront Costs. | Higher Upfront costs due to battery and storage. |
| 3. | Maintenance | Less Maintenance. | Higher Maintenance. |
| 4. | Suitability | Urban areas where the grid connection is stable | Remote areas where there isn’t any grid access |
Furthermore, let’s delve deeper into the comparison of On-grid vs Off-grid systems by considering additional factors such as energy storage, accessing electrical power, cost of solar power systems, equipment options resilience to power outages, solar installation costs, and challenges.
Energy Storage
Off-grid solar systems are completely dependent on batteries for energy storage since they aren’t connected to the utility grid. The excess energy is stored during the day and can be used during nights or periods of low sunlight.
On-grid solar systems do not require batteries for storage and have continuous access to the electricity grid. Also, the excess energy can be fed back into the grid and gain credits through net metering. However, there is an option to add batteries to store extra energy during power outages.
Accessing Electrical Power
Off-grid system doesn’t need any access to the electricity grid which means that the system generates electricity or gets charged by an external source. As a result, it becomes mandatory to use batteries to store additional electricity produced. During nights or cloudy days, the system uses the battery’s energy as the main power source.
On-grid system’s connection to the local utility means accessibility is possible except for blackouts. Here the utility grid acts as a power source when the electricity supplied from solar is insufficient.
Cost of Solar Power Systems
In an off-grid solar system, you can experience zero electricity bills once the setup is completed and paid. All you need to cover is the upfront cost of the equipment so that there wouldn’t be ongoing electricity bills as the system provides free power generated from sunlight.
The on-grid solar system connected to the utility grid provides a net metering option that helps homeowners receive credits on their electricity bills for excess energy generated by solar panels and feeding back to the grid. However, you need to pay a fixed charge for any utility services used such as grid connection and additional electricity costs for usage subtracted from the net metering credits.
Resilience to Power Outages
Off-grid systems are highly resilient against power outages and won’t affect electricity generation since they operate independently. As a result, you can enjoy non-stop electricity supply in prolonged blackouts being able to generate the required power for your needs.
As on-grid systems reliant on the utility grid, they aren’t resilient to power outages and any type of power failure interrupts the accessibility to electricity unless you don’t plan for a backup power system to store energy.
Costs of Solar Installations
On-grid solar systems have lower initial costs than off-grid ones as they don’t require additional components such as batteries or other backup sources to store extra power.
In contrast, off-grid systems result in long-term savings by minimizing the dependence on utility companies, thereby offering numerous benefits for the available tax credits and increasing prices of electricity.
Installation Challenges
For on-grid setups, the installation process is simple and less challenging due to minimal components. In contrast, the off-grid system installation process is more complicated to properly integrate batteries and inverters and involves high labor costs that require hiring highly skilled professionals during the installation process.
Equipment Options
The off-grid system uses solar panels, a DC-AC grid-tied solar inverter, battery storage, a backup generator, and a charge controller. Whereas, the on-grid system uses equipment such as solar panels, grid-tied inverters, utility meters (beneficial for net-metering systems), mounting systems, and electrical connections.
Should You Go Off Grid?
Yes, You can go off-grid, especially if you are seeking a solution to live a sustainable lifestyle. To consider changing to off-grid, with some drawbacks and factors, here are some of the primary reasons you must know.
- Environmental Benefits: The main motive to go off-grid is to reduce one’s carbon footprint. Also, minimizing greenhouse gas emissions contributes to a cleaner environment for future generations.
- Energy Independence: Using more solar power means more independence from using fossil fuels or relying on utility companies. And, this self-reliance can be very appealing in regions where the energy prices fluctuate.
- Resilience Against Power Outages: Off-grid systems come with a layer of protection against power outages that are caused due to severe weather, natural disasters, or critical infrastructure failures.
- Financial Benefits: Although the initial investment is higher, you will save a lot of money in the long run, especially benefitting from many federal and state incentives.
Despite such wonderful benefits, going off-grid has some drawbacks that are as follows:
- Equipment Failures: Many components are involved in off-grid systems and, if they fail to function properly, would lead to a loss of power.
- Maintenance Challenges: Off-grid system demands more maintenance than staying connected to the grid.
- Initial Costs: Although an off-grid system is the best for long-term saving, costlier investment at the initial stages will discourage many of them from opting for it.
Factors you must consider before going Off-Grid:
- Geographical Location.
- Assessing Energy Needs and Requirements.
- Researching Local Regulations regarding off-grid living to avoid restrictions.
An alternate for people who cannot fully go off-grid is opting for hybrid, which could be the best compromise. Solar panels work as primary energy generators during adequate sunlight, and the grid is just a backup during insufficient solar generation, allowing you to use energy generated from both sources.
What Type of Battery Should I Use When Going Off Grid?
Lithium Iron Phosphate is highly recommended while going off-grid due to its higher efficiency and lifespan. However, you need to handle the higher initial costs than other battery types to gain additional benefits.
These types of batteries are ideal for use due to their ability to last 5,000 cycles or more, and having the ability to perform consistently in temperatures between -20 °C and 60 °C, thereby making them suitable for long-term use. Also, they are lighter and portable than lead-acid batteries which make the installation and transportation process simpler. Mainly, the higher Depth of Discharge (DoD) of upto 90% means that you can effectively make use of the stored energy without compromising its battery life.
What Type of Solar Panel Should I Use When Going Off Grid?
Monocrystalline solar panels are the best ones to use rather than polycrystalline while going off-grid due to these reasons:
- Higher efficiency (15% to 22%).
- Durability and Longer Lifespan (25 to 30 years).
- Space efficiency (Requires few monocrystalline panels) makes them suitable for complicated installation processes involved in off-grid systems.
- Better performance under high temperatures.
Finally, if you aren’t able to afford monocrystalline panels due to costly prices, then you can consider polycrystalline panels as the second option.
Ray is an avid reader and writer with over 25 years of experience serving various domestic and multinational private and public energy companies in the USA.